2024
|
Huret, C.; Ferraye, L.; David, A.; Mohamed, M.; Valentin, N.; Charlotte, F.; Savignac, M.; Goodhardt, M.; Guery, J. C.; Rougeulle, C.; Morey, C. Altered X-chromosome inactivation predisposes to autoimmunity Journal Article In: Sci Adv, vol. 10, no. 18, pp. eadn6537, 2024, ISSN: 2375-2548 (Electronic) 2375-2548 (Linking). @article{RN2487,
title = {Altered X-chromosome inactivation predisposes to autoimmunity},
author = {Huret, C. and Ferraye, L. and David, A. and Mohamed, M. and Valentin, N. and Charlotte, F. and Savignac, M. and Goodhardt, M. and Guery, J. C. and Rougeulle, C. and Morey, C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38701219},
doi = {10.1126/sciadv.adn6537},
issn = {2375-2548 (Electronic) 2375-2548 (Linking)},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {Sci Adv},
volume = {10},
number = {18},
pages = {eadn6537},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Chi, L.; Liu, C.; Gribonika, I.; Gschwend, J.; Corral, D.; Han, S. J.; Lim, A. I.; Rivera, C. A.; Link, V. M.; Wells, A. C.; Bouladoux, N.; Collins, N.; Lima-Junior, D. S.; Enamorado, M.; Rehermann, B.; Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C.; Tussiwand, R.; Schneider, C.; Belkaid, Y. Sexual dimorphism in skin immunity is mediated by an androgen-ILC2-dendritic cell axis Journal Article In: Science, vol. 384, no. 6692, pp. eadk6200, 2024, ISSN: 1095-9203 (Electronic) 0036-8075 (Linking). @article{RN2480,
title = {Sexual dimorphism in skin immunity is mediated by an androgen-ILC2-dendritic cell axis},
author = {Chi, L. and Liu, C. and Gribonika, I. and Gschwend, J. and Corral, D. and Han, S. J. and Lim, A. I. and Rivera, C. A. and Link, V. M. and Wells, A. C. and Bouladoux, N. and Collins, N. and Lima-Junior, D. S. and Enamorado, M. and Rehermann, B. and Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C. and Tussiwand, R. and Schneider, C. and Belkaid, Y.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38574174},
doi = {10.1126/science.adk6200},
issn = {1095-9203 (Electronic) 0036-8075 (Linking)},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {Science},
volume = {384},
number = {6692},
pages = {eadk6200},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2023
|
Youness, A.; Cenac, C.; Faz-Lopez, B.; Grunenwald, S.; Barrat, F. J.; Chaumeil, J.; Mejia, J. E.; Guery, J. C. TLR8 escapes X chromosome inactivation in human monocytes and CD4(+) T cells Journal Article In: Biol Sex Differ, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 60, 2023, ISSN: 2042-6410 (Electronic)
2042-6410 (Linking). @article{RN2418,
title = {TLR8 escapes X chromosome inactivation in human monocytes and CD4(+) T cells},
author = {Youness, A. and Cenac, C. and Faz-Lopez, B. and Grunenwald, S. and Barrat, F. J. and Chaumeil, J. and Mejia, J. E. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37723501},
doi = {10.1186/s13293-023-00544-5},
issn = {2042-6410 (Electronic)
2042-6410 (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Biol Sex Differ},
volume = {14},
number = {1},
pages = {60},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Renaudineau, Y.; Muller, S.; Hedrich, C. M.; Chauveau, D.; Belliere, J.; De Almeida, S.; Damoiseaux, J.; Scherlinger, M.; Guery, J. C.; Sailler, L.; Bost, C. Immunological and translational key challenges in systemic lupus erythematosus: A symposium update Journal Article In: J Transl Autoimmun, vol. 6, pp. 100199, 2023, ISSN: 2589-9090 (Electronic)
2589-9090 (Linking). @article{RN2417,
title = {Immunological and translational key challenges in systemic lupus erythematosus: A symposium update},
author = {Renaudineau, Y. and Muller, S. and Hedrich, C. M. and Chauveau, D. and Belliere, J. and De Almeida, S. and Damoiseaux, J. and Scherlinger, M. and Guery, J. C. and Sailler, L. and Bost, C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37065621},
doi = {10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100199},
issn = {2589-9090 (Electronic)
2589-9090 (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {J Transl Autoimmun},
volume = {6},
pages = {100199},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Miquel, C. H.; Faz-Lopez, B.; Guery, J. C. Influence of X chromosome in sex-biased autoimmune diseases Journal Article In: J Autoimmun, vol. 137, pp. 102992, 2023, ISSN: 1095-9157 (Electronic)
0896-8411 (Linking). @article{RN2416,
title = {Influence of X chromosome in sex-biased autoimmune diseases},
author = {Miquel, C. H. and Faz-Lopez, B. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36641351},
doi = {10.1016/j.jaut.2023.102992},
issn = {1095-9157 (Electronic)
0896-8411 (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {J Autoimmun},
volume = {137},
pages = {102992},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Miquel, C. H.; Abbas, F.; Cenac, C.; Foret-Lucas, C.; Guo, C.; Ducatez, M.; Joly, E.; Hou, B.; Guery, J. C. B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is required for neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 and pathogen-like COVID-19 vaccines Journal Article In: Eur J Immunol, pp. e2350437, 2023, ISSN: 1521-4141 (Electronic)
0014-2980 (Linking). @article{RN2415,
title = {B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is required for neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 and pathogen-like COVID-19 vaccines},
author = {Miquel, C. H. and Abbas, F. and Cenac, C. and Foret-Lucas, C. and Guo, C. and Ducatez, M. and Joly, E. and Hou, B. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37438976},
doi = {10.1002/eji.202350437},
issn = {1521-4141 (Electronic)
0014-2980 (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Eur J Immunol},
pages = {e2350437},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Giang, N.; Villeneuve, T.; Maire, K.; Mejia, J. E.; Guery, J. C.; Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. PKCalpha interacts with Ca(v) 1.3 calcium channels to promote the Ca(v) 1.2/Ca(v) 1.3 duo tuning Th2 functions Journal Article In: Allergy, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 879-882, 2023, ISSN: 1398-9995 (Electronic)
0105-4538 (Linking). @article{RN2414,
title = {PKCalpha interacts with Ca(v) 1.3 calcium channels to promote the Ca(v) 1.2/Ca(v) 1.3 duo tuning Th2 functions},
author = {Giang, N. and Villeneuve, T. and Maire, K. and Mejia, J. E. and Guery, J. C. and Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36478369},
doi = {10.1111/all.15611},
issn = {1398-9995 (Electronic)
0105-4538 (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Allergy},
volume = {78},
number = {3},
pages = {879-882},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Anesi, N.; Miquel, C. H.; Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C. The Influence of Sex Hormones and X Chromosome in Immune Responses Journal Article In: Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, vol. 441, pp. 21-59, 2023, ISSN: 0070-217X (Print)
0070-217X (Linking). @article{RN2413,
title = {The Influence of Sex Hormones and X Chromosome in Immune Responses},
author = {Anesi, N. and Miquel, C. H. and Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37695424},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-35139-6_2},
issn = {0070-217X (Print)
0070-217X (Linking)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Curr Top Microbiol Immunol},
volume = {441},
pages = {21-59},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2022
|
Cenac, C.; Ducatez, M. F.; Guery, J. C. Hydroxychloroquine inhibits proteolytic processing of endogenous TLR7 protein in human primary plasmacytoid dendritic cells Journal Article In: Eur J Immunol, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 54-61, 2022, ISSN: 1521-4141 (Electronic)
0014-2980 (Linking). @article{RN2062,
title = {Hydroxychloroquine inhibits proteolytic processing of endogenous TLR7 protein in human primary plasmacytoid dendritic cells},
author = {Cenac, C. and Ducatez, M. F. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34580855},
doi = {10.1002/eji.202149361},
issn = {1521-4141 (Electronic)
0014-2980 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Eur J Immunol},
volume = {52},
number = {1},
pages = {54-61},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Congy-Jolivet, N.; Cenac, C.; Dellacasagrande, J.; Puissant-Lubrano, B.; Apoil, P. A.; Guedj, K.; Abbas, F.; Laffont, S.; Sourdet, S.; Guyonnet, S.; Nourhashemi, F.; Guery, J. C.; Blancher, A. Monocytes are the main source of STING-mediated IFN-alpha production Journal Article In: EBioMedicine, vol. 80, pp. 104047, 2022, ISSN: 2352-3964 (Electronic) 2352-3964 (Linking). @article{RN2018,
title = {Monocytes are the main source of STING-mediated IFN-alpha production},
author = {Congy-Jolivet, N. and Cenac, C. and Dellacasagrande, J. and Puissant-Lubrano, B. and Apoil, P. A. and Guedj, K. and Abbas, F. and Laffont, S. and Sourdet, S. and Guyonnet, S. and Nourhashemi, F. and Guery, J. C. and Blancher, A.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35561451},
doi = {10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104047},
issn = {2352-3964 (Electronic) 2352-3964 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {EBioMedicine},
volume = {80},
pages = {104047},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Abbas, F.; Cenac, C.; Youness, A.; Azar, P.; Delobel, P.; Guery, J. C. HIV-1 infection enhances innate function and TLR7 expression in female plasmacytoid dendritic cells Journal Article In: Life Sci Alliance, vol. 5, no. 10, 2022, ISSN: 2575-1077 (Electronic)
2575-1077 (Linking). @article{RN2065,
title = {HIV-1 infection enhances innate function and TLR7 expression in female plasmacytoid dendritic cells},
author = {Abbas, F. and Cenac, C. and Youness, A. and Azar, P. and Delobel, P. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36271499},
doi = {10.26508/lsa.202201452},
issn = {2575-1077 (Electronic)
2575-1077 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Life Sci Alliance},
volume = {5},
number = {10},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Giang, N.; Mars, M.; Moreau, M.; Mejia, J. E.; Bouchaud, G.; Magnan, A.; Michelet, M.; Ronsin, B.; Murphy, G. G.; Striessnig, J.; Guery, J. C.; Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. Separation of the Cav1.2-Cav1.3 calcium channel duo prevents type 2 allergic airway inflammation Journal Article In: Allergy, vol. 77, no. 2, pp. 525-539, 2022, ISSN: 1398-9995 (Electronic) 0105-4538 (Linking). @article{RN1997,
title = {Separation of the Cav1.2-Cav1.3 calcium channel duo prevents type 2 allergic airway inflammation},
author = {Giang, N. and Mars, M. and Moreau, M. and Mejia, J. E. and Bouchaud, G. and Magnan, A. and Michelet, M. and Ronsin, B. and Murphy, G. G. and Striessnig, J. and Guery, J. C. and Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34181765},
doi = {10.1111/all.14993},
issn = {1398-9995 (Electronic) 0105-4538 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Allergy},
volume = {77},
number = {2},
pages = {525-539},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Giang, N.; Villeneuve, T.; Maire, K.; Mejia, J. E.; Guery, J. C.; Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. PKCalpha interacts with Ca(v) 1.3 calcium channels to promote the Ca(v) 1.2/Ca(v) 1.3 duo tuning Th2 functions Journal Article In: Allergy, 2022, ISSN: 1398-9995 (Electronic) 0105-4538 (Linking). @article{RN2049,
title = {PKCalpha interacts with Ca(v) 1.3 calcium channels to promote the Ca(v) 1.2/Ca(v) 1.3 duo tuning Th2 functions},
author = {Giang, N. and Villeneuve, T. and Maire, K. and Mejia, J. E. and Guery, J. C. and Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36478369},
doi = {10.1111/all.15611},
issn = {1398-9995 (Electronic) 0105-4538 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Allergy},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Blanquart, E.; Mandonnet, A.; Mars, M.; Cenac, C.; Anesi, N.; Mercier, P.; Audouard, C.; Roga, S.; Serrano de Almeida, G.; Bevan, C. L.; Girard, J. P.; Pelletier, L.; Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C. Targeting androgen signaling in ILC2s protects from IL-33-driven lung inflammation, independently of KLRG1 Journal Article In: J Allergy Clin Immunol, vol. 149, no. 1, pp. 237-251 e12, 2022, ISSN: 1097-6825 (Electronic)
0091-6749 (Linking). @article{RN2428,
title = {Targeting androgen signaling in ILC2s protects from IL-33-driven lung inflammation, independently of KLRG1},
author = {Blanquart, E. and Mandonnet, A. and Mars, M. and Cenac, C. and Anesi, N. and Mercier, P. and Audouard, C. and Roga, S. and Serrano de Almeida, G. and Bevan, C. L. and Girard, J. P. and Pelletier, L. and Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33964300},
doi = {10.1016/j.jaci.2021.04.029},
issn = {1097-6825 (Electronic)
0091-6749 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {J Allergy Clin Immunol},
volume = {149},
number = {1},
pages = {237-251 e12},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Mars, M.; Neant, I.; Leclerc, C.; Bosch, S.; Rouviere, C.; Moreau, M.; Lachambre, S.; Paul, C.; Tauber, M.; Gravier, E.; Douzal, C.; Duplan, H.; Babin, M.; Brocario, A.; Thouvenin, M. D.; Guery, J. C.; Redoules, D.; Lestienne, F.; Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. Ca(v)1.4 calcium channels control cytokine production by human peripheral T(H)17 cells and psoriatic skin-infiltrating T cells Journal Article In: J Allergy Clin Immunol, vol. 149, no. 4, pp. 1348-1357, 2022, ISSN: 1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking). @article{RN2021,
title = {Ca(v)1.4 calcium channels control cytokine production by human peripheral T(H)17 cells and psoriatic skin-infiltrating T cells},
author = {Mars, M. and Neant, I. and Leclerc, C. and Bosch, S. and Rouviere, C. and Moreau, M. and Lachambre, S. and Paul, C. and Tauber, M. and Gravier, E. and Douzal, C. and Duplan, H. and Babin, M. and Brocario, A. and Thouvenin, M. D. and Guery, J. C. and Redoules, D. and Lestienne, F. and Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34653514},
doi = {10.1016/j.jaci.2021.09.030},
issn = {1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {J Allergy Clin Immunol},
volume = {149},
number = {4},
pages = {1348-1357},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Bost, C.; Arleevskaya, M. I.; Brooks, W. H.; Plaza, S.; Guery, J. C.; Renaudineau, Y. Long non-coding RNA Xist contribution in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis Journal Article In: Clin Immunol, vol. 236, pp. 108937, 2022, ISSN: 1521-7035 (Electronic)
1521-6616 (Linking). @article{RN2429,
title = {Long non-coding RNA Xist contribution in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis},
author = {Bost, C. and Arleevskaya, M. I. and Brooks, W. H. and Plaza, S. and Guery, J. C. and Renaudineau, Y.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35114365},
doi = {10.1016/j.clim.2022.108937},
issn = {1521-7035 (Electronic)
1521-6616 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Clin Immunol},
volume = {236},
pages = {108937},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Corral, D.; Charton, A.; Krauss, M. Z.; Blanquart, E.; Levillain, F.; Lefrancais, E.; Sneperger, T.; Vahlas, Z.; Girard, J. P.; Eberl, G.; Poquet, Y.; Guery, J. C.; Arguello, R. J.; Belkaid, Y.; Mayer-Barber, K. D.; Hepworth, M. R.; Neyrolles, O.; Hudrisier, D. ILC precursors differentiate into metabolically distinct ILC1-like cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection Journal Article In: Cell Rep, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 110715, 2022, ISSN: 2211-1247 (Electronic). @article{RN2430,
title = {ILC precursors differentiate into metabolically distinct ILC1-like cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection},
author = {Corral, D. and Charton, A. and Krauss, M. Z. and Blanquart, E. and Levillain, F. and Lefrancais, E. and Sneperger, T. and Vahlas, Z. and Girard, J. P. and Eberl, G. and Poquet, Y. and Guery, J. C. and Arguello, R. J. and Belkaid, Y. and Mayer-Barber, K. D. and Hepworth, M. R. and Neyrolles, O. and Hudrisier, D.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35443177},
doi = {10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110715},
issn = {2211-1247 (Electronic)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Cell Rep},
volume = {39},
number = {3},
pages = {110715},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2021
|
Youness, A.; Miquel, C. H.; Guéry, J. C. Escape from X Chromosome Inactivation and the Female Predominance in Autoimmune Diseases Journal Article In: Int J Mol Sci, vol. 22, no. 3, 2021, ISSN: 1422-0067. @article{RN1937,
title = {Escape from X Chromosome Inactivation and the Female Predominance in Autoimmune Diseases},
author = {Youness, A. and Miquel, C. H. and Guéry, J. C.},
doi = {10.3390/ijms22031114},
issn = {1422-0067},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Int J Mol Sci},
volume = {22},
number = {3},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Blanquart, E.; Mandonnet, A.; Mars, M.; Cenac, C.; Anesi, N.; Mercier, P.; Audouard, C.; Roga, S.; Serrano de Almeida, G.; Bevan, C. L.; Girard, J. P.; Pelletier, L.; Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C. Targeting androgen signaling in ILC2s protects from IL-33-driven lung inflammation, independently of KLRG1 Journal Article In: J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2021, ISSN: 1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking). @article{RN1947,
title = {Targeting androgen signaling in ILC2s protects from IL-33-driven lung inflammation, independently of KLRG1},
author = {Blanquart, E. and Mandonnet, A. and Mars, M. and Cenac, C. and Anesi, N. and Mercier, P. and Audouard, C. and Roga, S. and Serrano de Almeida, G. and Bevan, C. L. and Girard, J. P. and Pelletier, L. and Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33964300},
doi = {10.1016/j.jaci.2021.04.029},
issn = {1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {J Allergy Clin Immunol},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Cenac, C.; Ducatez, M.; Guery, J. C. Hydroxychloroquine inhibits proteolytic processing of endogenous TLR7 protein in human primary plasmacytoid dendritic cells Journal Article In: Eur J Immunol, 2021, ISSN: 1521-4141 (Electronic) 0014-2980 (Linking). @article{RN1956,
title = {Hydroxychloroquine inhibits proteolytic processing of endogenous TLR7 protein in human primary plasmacytoid dendritic cells},
author = {Cenac, C. and Ducatez, M. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34580855},
doi = {10.1002/eji.202149361},
issn = {1521-4141 (Electronic) 0014-2980 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Eur J Immunol},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Blanquart, E.; Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C. Sex hormone regulation of innate lymphoid cells Journal Article In: Biomed J, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 144-156, 2021, ISSN: 2320-2890 (Electronic)
2319-4170 (Linking). @article{RN1948,
title = {Sex hormone regulation of innate lymphoid cells},
author = {Blanquart, E. and Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33888441},
doi = {10.1016/j.bj.2020.11.007},
issn = {2320-2890 (Electronic)
2319-4170 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Biomed J},
volume = {44},
number = {2},
pages = {144-156},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2020
|
Pelletier, L.; Guéry, J. C. [Asthma and allergy: what about the differences between men and women?] Journal Article In: Rev Prat, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 195-199, 2020, ISSN: 0035-2640. @article{RN1939,
title = {[Asthma and allergy: what about the differences between men and women?]},
author = {Pelletier, L. and Guéry, J. C.},
issn = {0035-2640},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Rev Prat},
volume = {70},
number = {2},
pages = {195-199},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Azar, P.; Mejía, J. E.; Cenac, C.; Shaiykova, A.; Youness, A.; Laffont, S.; Essat, A.; Izopet, J.; Passaes, C.; Müller-Trutwin, M.; Delobel, P.; Meyer, L.; Guéry, J. C. TLR7 dosage polymorphism shapes interferogenesis and HIV-1 acute viremia in women Journal Article In: JCI Insight, vol. 5, no. 12, 2020, ISSN: 2379-3708. @article{RN1940,
title = {TLR7 dosage polymorphism shapes interferogenesis and HIV-1 acute viremia in women},
author = {Azar, P. and Mejía, J. E. and Cenac, C. and Shaiykova, A. and Youness, A. and Laffont, S. and Essat, A. and Izopet, J. and Passaes, C. and Müller-Trutwin, M. and Delobel, P. and Meyer, L. and Guéry, J. C.},
doi = {10.1172/jci.insight.136047},
issn = {2379-3708},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
journal = {JCI Insight},
volume = {5},
number = {12},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2019
|
Guery, Jean-Charles Why is systemic lupus erythematosus more common in women? Journal Article In: Joint Bone Spine, vol. 86, no. 3, pp. 297-299, 2019, (invited editorial). @article{Guery:2019aa,
title = {Why is systemic lupus erythematosus more common in women?},
author = {Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhum.2018.10.001},
doi = {10.1016/j.jbspin.2018.12.004},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-05-01},
journal = {Joint Bone Spine},
volume = {86},
number = {3},
pages = {297-299},
address = {Centre de Physiopathologie de Toulouse Purpan, Universite de Toulouse, INSERM, CNRS, Universite Paul Sabatier, 31300 Toulouse, France.},
note = {invited editorial},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Souyris, Melanie; Mejia, Jose E; Chaumeil, Julie; Guery, Jean-Charles Female predisposition to TLR7-driven autoimmunity: gene dosage and the escape from X chromosome inactivation. Journal Article In: Semin Immunopathol, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 153-164, 2019, ISSN: 1863-2300 (Electronic); 1863-2297 (Linking), (review). @article{Souyris:2018aa,
title = {Female predisposition to TLR7-driven autoimmunity: gene dosage and the escape from X chromosome inactivation.},
author = {Melanie Souyris and Jose E Mejia and Julie Chaumeil and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-018-0712-y},
doi = {10.1007/s00281-018-0712-y},
issn = {1863-2300 (Electronic); 1863-2297 (Linking)},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-03-01},
journal = {Semin Immunopathol},
volume = {41},
number = {2},
pages = {153-164},
address = {Centre de Physiopathologie de Toulouse Purpan (CPTP), Universite de Toulouse, INSERM, CNRS, Universite Paul Sabatier, 31300, Toulouse, France.},
abstract = {Women develop stronger immune responses than men, with positive effects on the resistance to viral or bacterial infections but magnifying also the susceptibility to autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In SLE, the dosage of the endosomal Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) is crucial. Murine models have shown that TLR7 overexpression suffices to induce spontaneous lupus-like disease. Conversely, suppressing TLR7 in lupus-prone mice abolishes SLE development. TLR7 is encoded by a gene on the X chromosome gene, denoted TLR7 in humans and Tlr7 in the mouse, and expressed in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC), monocytes/macrophages, and B cells. The receptor recognizes single-stranded RNA, and its engagement promotes B cell maturation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and antibodies. In female mammals, each cell randomly inactivates one of its two X chromosomes to equalize gene dosage with XY males. However, 15 to 23% of X-linked human genes escape X chromosome inactivation so that both alleles can be expressed simultaneously. It has been hypothesized that biallelic expression of X-linked genes could occur in female immune cells, hence fostering harmful autoreactive and inflammatory responses. We review here the current knowledge of the role of TLR7 in SLE, and recent evidence demonstrating that TLR7 escapes from X chromosome inactivation in pDCs, monocytes, and B lymphocytes from women and Klinefelter syndrome men. Female B cells where TLR7 is thus biallelically expressed display higher TLR7-driven functional responses, connecting the presence of two X chromosomes with the enhanced immunity of women and their increased susceptibility to TLR7-dependent autoimmune syndromes.},
note = {review},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Women develop stronger immune responses than men, with positive effects on the resistance to viral or bacterial infections but magnifying also the susceptibility to autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In SLE, the dosage of the endosomal Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) is crucial. Murine models have shown that TLR7 overexpression suffices to induce spontaneous lupus-like disease. Conversely, suppressing TLR7 in lupus-prone mice abolishes SLE development. TLR7 is encoded by a gene on the X chromosome gene, denoted TLR7 in humans and Tlr7 in the mouse, and expressed in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC), monocytes/macrophages, and B cells. The receptor recognizes single-stranded RNA, and its engagement promotes B cell maturation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and antibodies. In female mammals, each cell randomly inactivates one of its two X chromosomes to equalize gene dosage with XY males. However, 15 to 23% of X-linked human genes escape X chromosome inactivation so that both alleles can be expressed simultaneously. It has been hypothesized that biallelic expression of X-linked genes could occur in female immune cells, hence fostering harmful autoreactive and inflammatory responses. We review here the current knowledge of the role of TLR7 in SLE, and recent evidence demonstrating that TLR7 escapes from X chromosome inactivation in pDCs, monocytes, and B lymphocytes from women and Klinefelter syndrome men. Female B cells where TLR7 is thus biallelically expressed display higher TLR7-driven functional responses, connecting the presence of two X chromosomes with the enhanced immunity of women and their increased susceptibility to TLR7-dependent autoimmune syndromes. |
Garnier, A.; Laffont, S.; Garnier, L.; Kaba, E.; Deutsch, U.; Engelhardt, B.; Guery, J. C. CD49d/CD29-integrin controls the accumulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells into the CNS during neuroinflammation Journal Article In: Eur J Immunol, 2019, ISSN: 0014-2980. @article{RN3085,
title = {CD49d/CD29-integrin controls the accumulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells into the CNS during neuroinflammation},
author = {Garnier, A. and Laffont, S. and Garnier, L. and Kaba, E. and Deutsch, U. and Engelhardt, B. and Guery, J. C.},
doi = {10.1002/eji.201948086},
issn = {0014-2980},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Eur J Immunol},
abstract = {Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are found in the CNS during neuroinflammation and have been reported to exert regulatory functions in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). However, the mechanisms of entry of pDCs into the CNS as well as their phenotype and innate functional properties, once recruited into the CNS, have not been thoroughly examined. Herein, we show that pDCs rapidly accumulate into the brain and spinal cord during the acute phase of EAE, and maintain the expression of numerous phenotypic markers typical of peripheral pDCs. Functionally, CNS-pDCs constitutively expressed IRF7 and were able to rapidly produce type I IFNs and IL-12p40 upon ex vivo TLR-9 stimulation. Using adoptive transfer exper- iments, we provide evidence that CNS-pDC are recruited from the blood and accumulate into the CNS during the acute phase of EAE. Accumulation of pDCs into the CNS was strongly inhibited in the absence of CD29, but not CD18, suggesting a major role for ß1 but not ß2 integrins. Indeed, blocking the CD49d α4-integrins during acute EAE drastically diminished CNS-pDC numbers. Together, our results demonstrate that circulating pDCs are actively recruited into the CNS during acute EAE through a mechanism largely dependent on CD49d/CD29-integrins.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are found in the CNS during neuroinflammation and have been reported to exert regulatory functions in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). However, the mechanisms of entry of pDCs into the CNS as well as their phenotype and innate functional properties, once recruited into the CNS, have not been thoroughly examined. Herein, we show that pDCs rapidly accumulate into the brain and spinal cord during the acute phase of EAE, and maintain the expression of numerous phenotypic markers typical of peripheral pDCs. Functionally, CNS-pDCs constitutively expressed IRF7 and were able to rapidly produce type I IFNs and IL-12p40 upon ex vivo TLR-9 stimulation. Using adoptive transfer exper- iments, we provide evidence that CNS-pDC are recruited from the blood and accumulate into the CNS during the acute phase of EAE. Accumulation of pDCs into the CNS was strongly inhibited in the absence of CD29, but not CD18, suggesting a major role for ß1 but not ß2 integrins. Indeed, blocking the CD49d α4-integrins during acute EAE drastically diminished CNS-pDC numbers. Together, our results demonstrate that circulating pDCs are actively recruited into the CNS during acute EAE through a mechanism largely dependent on CD49d/CD29-integrins. |
Laffont, S.; Guery, J. C. Deconstructing the sex bias in allergy and autoimmunity: From sex hormones and beyond Journal Article In: Adv Immunol, vol. 142, pp. 35-64, 2019, ISSN: 0065-2776, (review). @article{RN3086,
title = {Deconstructing the sex bias in allergy and autoimmunity: From sex hormones and beyond},
author = {Laffont, S. and Guery, J. C.},
doi = {10.1016/bs.ai.2019.04.001},
issn = {0065-2776},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Adv Immunol},
volume = {142},
pages = {35-64},
abstract = {Men and women differ in their susceptibility to develop autoimmunity and allergy but also in their capacity to cope with infections. Mechanisms responsible for this sexual dimorphism are still poorly documented and probably multifactorial. This review discusses the recent development in our understanding of the cell-intrinsic actions of biological factors linked to sex, sex hormones and sex chromosome complement, on immune cells, which may account for the sex differences in the enhanced susceptibility of women to develop immunological disorders, such as allergic asthma or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We choose to more specifically discuss the impact of sex hormones on the development and function of immune cell populations directly involved in type-2 immunity, and the role of the X-linked Toll like receptor 7 (TLR7) in anti-viral immunity and in SLE. We will also elaborate on the recent evidence demonstrating that TLR7 escapes from X chromosome inactivation in the immune cells of women, and how this may contribute to endow woman immune system with enhanced responsiveness to RNA-virus and susceptibility to SLE.},
note = {review},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Men and women differ in their susceptibility to develop autoimmunity and allergy but also in their capacity to cope with infections. Mechanisms responsible for this sexual dimorphism are still poorly documented and probably multifactorial. This review discusses the recent development in our understanding of the cell-intrinsic actions of biological factors linked to sex, sex hormones and sex chromosome complement, on immune cells, which may account for the sex differences in the enhanced susceptibility of women to develop immunological disorders, such as allergic asthma or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We choose to more specifically discuss the impact of sex hormones on the development and function of immune cell populations directly involved in type-2 immunity, and the role of the X-linked Toll like receptor 7 (TLR7) in anti-viral immunity and in SLE. We will also elaborate on the recent evidence demonstrating that TLR7 escapes from X chromosome inactivation in the immune cells of women, and how this may contribute to endow woman immune system with enhanced responsiveness to RNA-virus and susceptibility to SLE. |
Domingo, Cristina; Fraissinet, Juliane; Ansah, Patrick O.; Kelly, Corey; Bhat, Niranjan; Sow, Samba O.; Mejía, José E. Long-term immunity against yellow fever in children vaccinated during infancy: a longitudinal cohort study Journal Article In: Lancet Infect Dis, 2019, ISSN: 1473-3099. @article{RN3090,
title = {Long-term immunity against yellow fever in children vaccinated during infancy: a longitudinal cohort study},
author = {Domingo, Cristina and Fraissinet, Juliane and Ansah, Patrick O. and Kelly, Corey and Bhat, Niranjan and Sow, Samba O. and Mejía, José E.},
doi = {10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30323-8},
issn = {1473-3099},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Lancet Infect Dis},
abstract = {Background. A single dose of vaccine against yellow fever is routinely administered to infants aged 9–12 months under the Expanded Programme on Immunization, but the long-term outcome of vaccination in this age group is unknown. We aimed to evaluate the long-term persistence of neutralising antibodies to yellow fever virus following routine vaccination in infancy.
Methods. We did a longitudinal cohort study, using a microneutralisation assay to measure protective antibodies against yellow fever in Malian and Ghanaian children vaccinated around age 9 months and followed up for 4·5 years (Mali), or 2·3 and 6·0 years (Ghana). Healthy children with available day-0 sera, a complete follow-up history, and no record of yellow fever revaccination were included; children seropositive for yellow fever at baseline were excluded. We standardised antibody concentrations with reference to the yellow fever WHO International Standard.
Findings. We included 587 Malian and 436 Ghanaian children vaccinated between June 5, 2009, and Dec 26, 2012. In the Malian group, 296 (50·4%, 95% CI 46·4–54·5) were seropositive (antibody concentration ≥0·5 IU/mL) 4·5 years after vaccination. Among the Ghanaian children, 121 (27·8%, 23·5–32·0) were seropositive after 2·3 years. These results show a large decrease from the proportions of seropositive infants 28 days after vaccination, 96·7% in Mali and 72·7% in Ghana, reported by a previous study of both study populations. The number of seropositive children increased to 188 (43·1%, 95% CI 38·5–47·8) in the Ghanaian group 6·0 years after vaccination, but this result might be confounded by unrecorded revaccination or natural infection with wild yellow fever virus during a 2011–12 outbreak in northern Ghana.
Interpretation. Rapid waning of immunity during the early years after vaccination of 9-month-old infants argues for a revision of the single-dose recommendation for this target population in endemic countries. The short duration of immunity in many vaccinees suggests that booster vaccination is necessary to meet the 80% population immunity threshold for prevention of yellow fever outbreaks.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Background. A single dose of vaccine against yellow fever is routinely administered to infants aged 9–12 months under the Expanded Programme on Immunization, but the long-term outcome of vaccination in this age group is unknown. We aimed to evaluate the long-term persistence of neutralising antibodies to yellow fever virus following routine vaccination in infancy.
Methods. We did a longitudinal cohort study, using a microneutralisation assay to measure protective antibodies against yellow fever in Malian and Ghanaian children vaccinated around age 9 months and followed up for 4·5 years (Mali), or 2·3 and 6·0 years (Ghana). Healthy children with available day-0 sera, a complete follow-up history, and no record of yellow fever revaccination were included; children seropositive for yellow fever at baseline were excluded. We standardised antibody concentrations with reference to the yellow fever WHO International Standard.
Findings. We included 587 Malian and 436 Ghanaian children vaccinated between June 5, 2009, and Dec 26, 2012. In the Malian group, 296 (50·4%, 95% CI 46·4–54·5) were seropositive (antibody concentration ≥0·5 IU/mL) 4·5 years after vaccination. Among the Ghanaian children, 121 (27·8%, 23·5–32·0) were seropositive after 2·3 years. These results show a large decrease from the proportions of seropositive infants 28 days after vaccination, 96·7% in Mali and 72·7% in Ghana, reported by a previous study of both study populations. The number of seropositive children increased to 188 (43·1%, 95% CI 38·5–47·8) in the Ghanaian group 6·0 years after vaccination, but this result might be confounded by unrecorded revaccination or natural infection with wild yellow fever virus during a 2011–12 outbreak in northern Ghana.
Interpretation. Rapid waning of immunity during the early years after vaccination of 9-month-old infants argues for a revision of the single-dose recommendation for this target population in endemic countries. The short duration of immunity in many vaccinees suggests that booster vaccination is necessary to meet the 80% population immunity threshold for prevention of yellow fever outbreaks.
|
2018
|
Garnier, Laure; Laffont, Sophie; Lelu, Karine; Yogev, Nir; Waisman, Ari; Guery, Jean-Charles Estrogen Signaling in Bystander Foxp3(neg) CD4(+) T Cells Suppresses Cognate Th17 Differentiation in Trans and Protects from Central Nervous System Autoimmunity. Journal Article In: J Immunol, vol. 201, no. 11, pp. 3218–3228, 2018, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic); 0022-1767 (Linking). @article{Garnier:2018aa,
title = {Estrogen Signaling in Bystander Foxp3(neg) CD4(+) T Cells Suppresses Cognate Th17 Differentiation in Trans and Protects from Central Nervous System Autoimmunity.},
author = {Laure Garnier and Sophie Laffont and Karine Lelu and Nir Yogev and Ari Waisman and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1800417 },
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1800417},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic); 0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-12-01},
journal = {J Immunol},
volume = {201},
number = {11},
pages = {3218--3228},
address = {Centre de Physiopathologie de Toulouse Purpan, Universite de Toulouse, INSERM, CNRS, Universite Paul Sabatier, 31300 Toulouse, France.},
abstract = {17beta-Estradiol (E2) suppresses the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) through estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, yet the cellular targets remain elusive. We have used an adoptive transfer model of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific CD4(+) T cells from 2D2 TCR transgenic mice. We show that in the recipient mice, ERalpha expression in bystander CD4(+) T cells, rather than in cognate 2D2 T cells, is required for the inhibition of Th17 cell differentiation by E2. Coadministration of estrogen-primed WT, but not ERalpha-deficient CD4(+) T cells, with naive 2D2 T cells lacking ERalpha inhibited the development of Th17 cell-mediated EAE. Suppression of Th17 cells and protection from EAE were maintained when ERalpha was deleted in Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. We showed that in vivo PD-L1 blockade alleviated the anti-inflammatory action of E2 and that PD-1 expression on cognate but not bystander T cells was required for the E2-dependent inhibition of Th17 differentiation. In cotransfer experiments, we found that only WT but not PD-1(KO) 2D2 T cells were amenable to E2-dependent inhibition of Th17 differentiation. These results support the conclusion that the restriction of Th17 cell development by E2-primed bystander CD4(+) T cells requires cell-intrinsic PD-1 signaling within cognate T cells rather than induction of regulatory 2D2 T cells through PD-1 engagement. Altogether, our results indicate that pregnancy-level concentrations of estrogen signal in conventional Foxp3(neg) CD4(+) T cells to limit the differentiation of cognate Th17 cells through a trans-acting mechanism of suppression that requires a functional PD-1/PD-L1 regulatory axis.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
17beta-Estradiol (E2) suppresses the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) through estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, yet the cellular targets remain elusive. We have used an adoptive transfer model of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific CD4(+) T cells from 2D2 TCR transgenic mice. We show that in the recipient mice, ERalpha expression in bystander CD4(+) T cells, rather than in cognate 2D2 T cells, is required for the inhibition of Th17 cell differentiation by E2. Coadministration of estrogen-primed WT, but not ERalpha-deficient CD4(+) T cells, with naive 2D2 T cells lacking ERalpha inhibited the development of Th17 cell-mediated EAE. Suppression of Th17 cells and protection from EAE were maintained when ERalpha was deleted in Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. We showed that in vivo PD-L1 blockade alleviated the anti-inflammatory action of E2 and that PD-1 expression on cognate but not bystander T cells was required for the E2-dependent inhibition of Th17 differentiation. In cotransfer experiments, we found that only WT but not PD-1(KO) 2D2 T cells were amenable to E2-dependent inhibition of Th17 differentiation. These results support the conclusion that the restriction of Th17 cell development by E2-primed bystander CD4(+) T cells requires cell-intrinsic PD-1 signaling within cognate T cells rather than induction of regulatory 2D2 T cells through PD-1 engagement. Altogether, our results indicate that pregnancy-level concentrations of estrogen signal in conventional Foxp3(neg) CD4(+) T cells to limit the differentiation of cognate Th17 cells through a trans-acting mechanism of suppression that requires a functional PD-1/PD-L1 regulatory axis. |
Rosa, N.; Triffaux, E.; Robert, V.; Mars, M.; Klein, M.; Bouchaud, G.; Canivet, A.; Magnan, A.; Guery, J. C.; Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. The beta and alpha2delta auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated calcium channel 1 (Cav1) are required for TH2 lymphocyte function and acute allergic airway inflammation Journal Article In: J Allergy Clin Immunol, vol. 142, no. 3, pp. 892-903, 2018, ISSN: 1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking). @article{RN24,
title = {The beta and alpha2delta auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated calcium channel 1 (Cav1) are required for TH2 lymphocyte function and acute allergic airway inflammation},
author = {Rosa, N. and Triffaux, E. and Robert, V. and Mars, M. and Klein, M. and Bouchaud, G. and Canivet, A. and Magnan, A. and Guery, J. C. and Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29129580
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091674917317402},
doi = {10.1016/j.jaci.2017.09.045},
issn = {1097-6825 (Electronic) 0091-6749 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-09-01},
journal = {J Allergy Clin Immunol},
volume = {142},
number = {3},
pages = {892-903},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Pelletier, Lucette; Savignac, Magali Involvement of ion channels in allergy Journal Article In: Current Opinion in Immunology, vol. 52, pp. 60 - 67, 2018, ISSN: 0952-7915, (review). @article{PELLETIER201860,
title = {Involvement of ion channels in allergy},
author = {Lucette Pelletier and Magali Savignac},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952791517301504},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2018.04.006},
issn = {0952-7915},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-06-01},
journal = {Current Opinion in Immunology},
volume = {52},
pages = {60 - 67},
abstract = {Allergic asthma is a complex disease, often characterized by an inappropriate Th2 response to normally harmless allergens. Epithelial cells damaged or activated by the allergen produce IL-33, TSLP and IL-25, activating ILC2 and dendritic cells. The latter migrate into lymph nodes where they induce Th2-cell commitment. Th2 and other type 2 innate inflammatory cells trigger inflammation and airway hyper-reactivity. The toolbox consisting of the ion channels varies from one cellular type to another and depends on its activation state, offering the possibility to design novel drugs in the field of allergy. We will discuss about some channels as calcium, nonselective cation, potassium and chloride channels that appear as good candidates in allergy.},
note = {review},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Allergic asthma is a complex disease, often characterized by an inappropriate Th2 response to normally harmless allergens. Epithelial cells damaged or activated by the allergen produce IL-33, TSLP and IL-25, activating ILC2 and dendritic cells. The latter migrate into lymph nodes where they induce Th2-cell commitment. Th2 and other type 2 innate inflammatory cells trigger inflammation and airway hyper-reactivity. The toolbox consisting of the ion channels varies from one cellular type to another and depends on its activation state, offering the possibility to design novel drugs in the field of allergy. We will discuss about some channels as calcium, nonselective cation, potassium and chloride channels that appear as good candidates in allergy. |
Souyris, M.; Cenac, C.; Azar, P.; Daviaud, D.; Canivet, A.; Grunenwald, S.; Pienkowski, C.; Chaumeil, J.; Mejia, J. E.; Guery, J. C. TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells Journal Article In: Sci Immunol, vol. 3, no. 19, 2018, ISSN: 2470-9468 (Electronic) 2470-9468 (Linking), (In the top 5% of all research outputs scored by Altmetric. http://www.altmetric.com/details/32261033). @article{RN25b,
title = {TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells},
author = {Souyris, M. and Cenac, C. and Azar, P. and Daviaud, D. and Canivet, A. and Grunenwald, S. and Pienkowski, C. and Chaumeil, J. and Mejia, J. E. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29374079},
doi = {10.1126/sciimmunol.aap8855},
issn = {2470-9468 (Electronic) 2470-9468 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-26},
journal = {Sci Immunol},
volume = {3},
number = {19},
note = {In the top 5% of all research outputs scored by Altmetric. http://www.altmetric.com/details/32261033},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Blanquart, Eve; Laffont, Sophie; Guery, Jean-Charles Effets protecteurs de la puberte chez les garcons dans les maladies allergiques : les androgenes, un regulateur negatif des cellules lymphoides innees de groupe 2 Journal Article In: Rev Fr Allergol, vol. 5991, no. 4, pp. 297-357, 2018, ISSN: 1877-0320, (review). @article{Blanquart:2018aa,
title = {Effets protecteurs de la puberte chez les garcons dans les maladies allergiques : les androgenes, un regulateur negatif des cellules lymphoides innees de groupe 2},
author = {Eve Blanquart and Sophie Laffont and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877-0320(18)30273-2},
doi = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.reval.2018.02.220},
issn = {1877-0320},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Rev Fr Allergol},
volume = {5991},
number = {4},
pages = {297-357},
note = {review},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Laffont, Sophie; Blanquart, Eve; Guery, Jean-Charles Sex-bias in allergic asthma: androgens and group 2 innate lymphoid cells Journal Article In: Med Sci (Paris), vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 247-252, 2018, ISSN: 1958-5381 (Electronic) 0767-0974 (Linking), (review). @article{RN22b,
title = {Sex-bias in allergic asthma: androgens and group 2 innate lymphoid cells},
author = {Sophie Laffont and Eve Blanquart and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29547111},
doi = {10.1051/medsci/20183403013},
issn = {1958-5381 (Electronic) 0767-0974 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Med Sci (Paris)},
volume = {34},
number = {3},
pages = {247-252},
note = {review},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2017
|
Laffont, Sophie; Blanquart, Eve; Guery, Jean-Charles Sex Differences in Asthma: A Key Role of Androgen-Signaling in Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Journal Article In: Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 8, pp. 1069, 2017, ISSN: 1664-3224. @article{10.3389/fimmu.2017.01069,
title = {Sex Differences in Asthma: A Key Role of Androgen-Signaling in Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells},
author = {Sophie Laffont and Eve Blanquart and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01069},
doi = {10.3389/fimmu.2017.01069},
issn = {1664-3224},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Frontiers in Immunology},
volume = {8},
pages = {1069},
abstract = {Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases but also allergy differentially affect women and men. In general, women develop strongest immune responses and thus the proportion of infected individuals and the severity of many viral, bacterial or parasitic infections are increased in men. However, heightened immunity in women makes them more susceptible than men to autoimmunity and allergy. While sex differences in immunity are well documented, little is known about the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these immunological differences, particularly in allergic asthma. Asthma is a chronic inflammation of the airways mediated by exacerbated type 2 immune responses. Sex differences have been reported in the incidence, prevalence and severity of asthma. While during childhood, males are more susceptible to asthma than females, there is a switch at the onset of puberty as for many other allergic diseases. This decrease of asthma incidence around puberty in males suggests that hormonal mediators could play a protective role in the susceptibility to allergic responses in male. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) have recently emerged as critical players in the initiation of allergic responses, but also in the resolution of parasitic infection, through their capacity to rapidly and potently produce type 2 cytokines. This review will cover the current understanding of the impact of sex-linked factors in allergic inflammation, with a particular focus on the impact of sex hormones on the development and function of tissue-resident ILC2.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases but also allergy differentially affect women and men. In general, women develop strongest immune responses and thus the proportion of infected individuals and the severity of many viral, bacterial or parasitic infections are increased in men. However, heightened immunity in women makes them more susceptible than men to autoimmunity and allergy. While sex differences in immunity are well documented, little is known about the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these immunological differences, particularly in allergic asthma. Asthma is a chronic inflammation of the airways mediated by exacerbated type 2 immune responses. Sex differences have been reported in the incidence, prevalence and severity of asthma. While during childhood, males are more susceptible to asthma than females, there is a switch at the onset of puberty as for many other allergic diseases. This decrease of asthma incidence around puberty in males suggests that hormonal mediators could play a protective role in the susceptibility to allergic responses in male. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) have recently emerged as critical players in the initiation of allergic responses, but also in the resolution of parasitic infection, through their capacity to rapidly and potently produce type 2 cytokines. This review will cover the current understanding of the impact of sex-linked factors in allergic inflammation, with a particular focus on the impact of sex hormones on the development and function of tissue-resident ILC2. |
Laffont, Sophie; Blanquart, Eve; Savignac, Magali; Cenac, Claire; Laverny, Gilles; Metzger, Daniel; Girard, Jean-Philippe; Belz, Gabrielle T; Pelletier, Lucette; Seillet, Cyril; Guery, Jean-Charles Androgen signaling negatively controls group 2 innate lymphoid cells Journal Article In: J Exp Med, vol. 214, no. 6, pp. 1581-1592, 2017, ISSN: 1540-9538 (Electronic) 0022-1007 (Linking). @article{RN3,
title = {Androgen signaling negatively controls group 2 innate lymphoid cells},
author = {Sophie Laffont and Eve Blanquart and Magali Savignac and Claire Cenac and Gilles Laverny and Daniel Metzger and Jean-Philippe Girard and Gabrielle T Belz and Lucette Pelletier and Cyril Seillet and Jean-Charles Guery},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28484078},
doi = {10.1084/jem.20161807},
issn = {1540-9538 (Electronic) 0022-1007 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {J Exp Med},
volume = {214},
number = {6},
pages = {1581-1592},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Laffont, S.; Seillet, C.; Guery, J. C. Estrogen Receptor-Dependent Regulation of Dendritic Cell Development and Function Journal Article In: Front Immunol, vol. 8, pp. 108, 2017, ISSN: 1664-3224 (Linking). @article{RN6,
title = {Estrogen Receptor-Dependent Regulation of Dendritic Cell Development and Function},
author = {Laffont, S. and Seillet, C. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28239379},
doi = {10.3389/fimmu.2017.00108},
issn = {1664-3224 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Front Immunol},
volume = {8},
pages = {108},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Basso, L.; Garnier, L.; Bessac, A.; Boue, J.; Blanpied, C.; Cenac, N.; Laffont, S.; Dietrich, G. T-lymphocyte-derived enkephalins reduce Th1/Th17 colitis and associated pain in mice Journal Article In: J Gastroenterol, 2017, ISSN: 1435-5922 (Electronic)
0944-1174 (Linking). @article{RN11,
title = {T-lymphocyte-derived enkephalins reduce Th1/Th17 colitis and associated pain in mice},
author = {Basso, L. and Garnier, L. and Bessac, A. and Boue, J. and Blanpied, C. and Cenac, N. and Laffont, S. and Dietrich, G.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28424989},
doi = {10.1007/s00535-017-1341-2},
issn = {1435-5922 (Electronic)
0944-1174 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {J Gastroenterol},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2015
|
Griesbeck, M.; Ziegler, S.; Laffont, S.; Smith, N.; Chauveau, L.; Tomezsko, P.; Sharei, A.; Kourjian, G.; Porichis, F.; Hart, M.; Palmer, C. D.; Sirignano, M.; Beisel, C.; Hildebrandt, H.; Cenac, C.; Villani, A. C.; Diefenbach, T. J.; Le Gall, S.; Schwartz, O.; Herbeuval, J. P.; Autran, B.; Guery, J. C.; Chang, J. J.; Altfeld, M. Sex Differences in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Levels of IRF5 Drive Higher IFN-alpha Production in Women Journal Article In: J Immunol, vol. 195, no. 11, pp. 5327-36, 2015, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking). @article{RN1b,
title = {Sex Differences in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Levels of IRF5 Drive Higher IFN-alpha Production in Women},
author = {Griesbeck, M. and Ziegler, S. and Laffont, S. and Smith, N. and Chauveau, L. and Tomezsko, P. and Sharei, A. and Kourjian, G. and Porichis, F. and Hart, M. and Palmer, C. D. and Sirignano, M. and Beisel, C. and Hildebrandt, H. and Cenac, C. and Villani, A. C. and Diefenbach, T. J. and Le Gall, S. and Schwartz, O. and Herbeuval, J. P. and Autran, B. and Guery, J. C. and Chang, J. J. and Altfeld, M.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26519527},
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1501684},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {J Immunol},
volume = {195},
number = {11},
pages = {5327-36},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Laffont, S.; Garnier, L.; Lelu, K.; Guery, J. C. Estrogen-mediated protection of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Lessons from the dissection of estrogen receptor-signaling in vivo Journal Article In: Biomed J, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 194-205, 2015, ISSN: 2320-2890 (Electronic)
2319-4170 (Linking). @article{RN4,
title = {Estrogen-mediated protection of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Lessons from the dissection of estrogen receptor-signaling in vivo},
author = {Laffont, S. and Garnier, L. and Lelu, K. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26068028},
doi = {10.4103/2319-4170.158509},
issn = {2320-2890 (Electronic)
2319-4170 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {Biomed J},
volume = {38},
number = {3},
pages = {194-205},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Lupar, E.; Brack, M.; Garnier, L.; Laffont, S.; Rauch, K. S.; Schachtrup, K.; Arnold, S. J.; Guery, J. C.; Izcue, A. Eomesodermin Expression in CD4+ T Cells Restricts Peripheral Foxp3 Induction Journal Article In: J Immunol, vol. 195, no. 10, pp. 4742-52, 2015, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking). @article{RN7,
title = {Eomesodermin Expression in CD4+ T Cells Restricts Peripheral Foxp3 Induction},
author = {Lupar, E. and Brack, M. and Garnier, L. and Laffont, S. and Rauch, K. S. and Schachtrup, K. and Arnold, S. J. and Guery, J. C. and Izcue, A.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26453746},
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1501159},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {J Immunol},
volume = {195},
number = {10},
pages = {4742-52},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2014
|
Savignac, M.; Simon, M.; Edir, A.; Guibbal, L.; Hovnanian, A. SERCA2 dysfunction in Darier disease causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and impaired cell-to-cell adhesion strength: rescue by Miglustat Journal Article In: J Invest Dermatol, vol. 134, no. 7, pp. 1961-1970, 2014, ISSN: 1523-1747 (Electronic)
0022-202X (Linking). @article{RN12b,
title = {SERCA2 dysfunction in Darier disease causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and impaired cell-to-cell adhesion strength: rescue by Miglustat},
author = {Savignac, M. and Simon, M. and Edir, A. and Guibbal, L. and Hovnanian, A.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24390139},
doi = {10.1038/jid.2014.8},
issn = {1523-1747 (Electronic)
0022-202X (Linking)},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {J Invest Dermatol},
volume = {134},
number = {7},
pages = {1961-1970},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Laffont, S.; Rouquie, N.; Azar, P.; Seillet, C.; Plumas, J.; Aspord, C.; Guery, J. C. X-Chromosome complement and estrogen receptor signaling independently contribute to the enhanced TLR7-mediated IFN-alpha production of plasmacytoid dendritic cells from women Journal Article In: J Immunol, vol. 193, no. 11, pp. 5444-52, 2014, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking). @article{RN5,
title = {X-Chromosome complement and estrogen receptor signaling independently contribute to the enhanced TLR7-mediated IFN-alpha production of plasmacytoid dendritic cells from women},
author = {Laffont, S. and Rouquie, N. and Azar, P. and Seillet, C. and Plumas, J. and Aspord, C. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25339659
http://www.jimmunol.org/content/193/11/5444.full.pdf},
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1303400},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {J Immunol},
volume = {193},
number = {11},
pages = {5444-52},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Mellstrom, B.; Sahun, I.; Ruiz-Nuno, A.; Murtra, P.; Gomez-Villafuertes, R.; Savignac, M.; Oliveros, J. C.; Gonzalez, P.; Kastanauskaite, A.; Knafo, S.; Zhuo, M.; Higuera-Matas, A.; Errington, M. L.; Maldonado, R.; DeFelipe, J.; Jefferys, J. G.; Bliss, T. V.; Dierssen, M.; Naranjo, J. R. DREAM controls the on/off switch of specific activity-dependent transcription pathways Journal Article In: Mol Cell Biol, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 877-87, 2014, ISSN: 1098-5549 (Electronic)
0270-7306 (Linking). @article{RN20b,
title = {DREAM controls the on/off switch of specific activity-dependent transcription pathways},
author = {Mellstrom, B. and Sahun, I. and Ruiz-Nuno, A. and Murtra, P. and Gomez-Villafuertes, R. and Savignac, M. and Oliveros, J. C. and Gonzalez, P. and Kastanauskaite, A. and Knafo, S. and Zhuo, M. and Higuera-Matas, A. and Errington, M. L. and Maldonado, R. and DeFelipe, J. and Jefferys, J. G. and Bliss, T. V. and Dierssen, M. and Naranjo, J. R.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24366545},
doi = {10.1128/MCB.00360-13},
issn = {1098-5549 (Electronic)
0270-7306 (Linking)},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {Mol Cell Biol},
volume = {34},
number = {5},
pages = {877-87},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Lucca, L. E.; Desbois, S.; Ramadan, A.; Ben-Nun, A.; Eisenstein, M.; Carrie, N.; Guery, J. C.; Sette, A.; Nguyen, P.; Geiger, T. L.; Mars, L. T.; Liblau, R. S. Bispecificity for myelin and neuronal self-antigens is a common feature of CD4 T cells in C57BL/6 mice Journal Article In: J Immunol, vol. 193, no. 7, pp. 3267-77, 2014, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking). @article{RN21,
title = {Bispecificity for myelin and neuronal self-antigens is a common feature of CD4 T cells in C57BL/6 mice},
author = {Lucca, L. E. and Desbois, S. and Ramadan, A. and Ben-Nun, A. and Eisenstein, M. and Carrie, N. and Guery, J. C. and Sette, A. and Nguyen, P. and Geiger, T. L. and Mars, L. T. and Liblau, R. S.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25135834},
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1400523},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {J Immunol},
volume = {193},
number = {7},
pages = {3267-77},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2013
|
Pelletier, L.; Savignac, M. Ca(2+) signaling in T-cell subsets with a focus on the role of cav1 channels: possible implications in therapeutics Journal Article In: Front Immunol, vol. 4, pp. 150, 2013, ISSN: 1664-3224 (Print)
1664-3224 (Linking). @article{RN15,
title = {Ca(2+) signaling in T-cell subsets with a focus on the role of cav1 channels: possible implications in therapeutics},
author = {Pelletier, L. and Savignac, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23801988},
doi = {10.3389/fimmu.2013.00150},
issn = {1664-3224 (Print)
1664-3224 (Linking)},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Front Immunol},
volume = {4},
pages = {150},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Robert, V.; Triffaux, E.; Savignac, M.; Pelletier, L. Singularities of calcium signaling in effector T-lymphocytes Journal Article In: Biochim Biophys Acta, vol. 1833, no. 7, pp. 1595-602, 2013, ISSN: 0006-3002 (Print)
0006-3002 (Linking). @article{RN16b,
title = {Singularities of calcium signaling in effector T-lymphocytes},
author = {Robert, V. and Triffaux, E. and Savignac, M. and Pelletier, L.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23266355},
doi = {10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.12.001},
issn = {0006-3002 (Print)
0006-3002 (Linking)},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Biochim Biophys Acta},
volume = {1833},
number = {7},
pages = {1595-602},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Seillet, C.; Rouquie, N.; Foulon, E.; Douin-Echinard, V.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; Arnal, J. F.; Guery, J. C.; Laffont, S. Estradiol Promotes Functional Responses in Inflammatory and Steady-State Dendritic Cells through Differential Requirement for Activation Function-1 of Estrogen Receptor alpha Journal Article In: J. Immunol., vol. 190, no. 11, pp. 5459-70, 2013, ISSN: 1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking). @article{RN10b,
title = {Estradiol Promotes Functional Responses in Inflammatory and Steady-State Dendritic Cells through Differential Requirement for Activation Function-1 of Estrogen Receptor alpha},
author = {Seillet, C. and Rouquie, N. and Foulon, E. and Douin-Echinard, V. and Krust, A. and Chambon, P. and Arnal, J. F. and Guery, J. C. and Laffont, S.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23626011
http://www.jimmunol.org/content/190/11/5459.full.pdf},
doi = {10.4049/jimmunol.1203312},
issn = {1550-6606 (Electronic)
0022-1767 (Linking)},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {J. Immunol.},
volume = {190},
number = {11},
pages = {5459-70},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2012
|
Pendaries, V.; Gasc, G.; Titeux, M.; Tonasso, L.; Mejia, J. E.; Hovnanian, A. siRNA-mediated allele-specific inhibition of mutant type VII collagen in dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa Journal Article In: J Invest Dermatol, vol. 132, no. 6, pp. 1741-3, 2012, ISSN: 1523-1747 (Electronic)
0022-202X (Linking). @article{RN17b,
title = {siRNA-mediated allele-specific inhibition of mutant type VII collagen in dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa},
author = {Pendaries, V. and Gasc, G. and Titeux, M. and Tonasso, L. and Mejia, J. E. and Hovnanian, A.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22336946},
doi = {10.1038/jid.2012.11},
issn = {1523-1747 (Electronic)
0022-202X (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {J Invest Dermatol},
volume = {132},
number = {6},
pages = {1741-3},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Pernet, C.; Bessis, D.; Savignac, M.; Tron, E.; Guillot, B.; Hovnanian, A. Genitoperineal papular acantholytic dyskeratosis is allelic to Hailey-Hailey disease Journal Article In: Br J Dermatol, vol. 167, no. 1, pp. 210-2, 2012, ISSN: 1365-2133 (Electronic)
0007-0963 (Linking). @article{RN19b,
title = {Genitoperineal papular acantholytic dyskeratosis is allelic to Hailey-Hailey disease},
author = {Pernet, C. and Bessis, D. and Savignac, M. and Tron, E. and Guillot, B. and Hovnanian, A.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22229453},
doi = {10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10810.x},
issn = {1365-2133 (Electronic)
0007-0963 (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Br J Dermatol},
volume = {167},
number = {1},
pages = {210-2},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Robert, V.; Triffaux, E.; Savignac, M.; Pelletier, L. [Calcium signaling in T lymphocytes] Journal Article In: Med Sci (Paris), vol. 28, no. 8-9, pp. 773-9, 2012, ISSN: 0767-0974 (Print)
0767-0974 (Linking). @article{RN13b,
title = {[Calcium signaling in T lymphocytes]},
author = {Robert, V. and Triffaux, E. and Savignac, M. and Pelletier, L.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22920880},
doi = {10.1051/medsci/2012288020},
issn = {0767-0974 (Print)
0767-0974 (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Med Sci (Paris)},
volume = {28},
number = {8-9},
pages = {773-9},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Seillet, C.; Laffont, S.; Tremollieres, F.; Rouquie, N.; Ribot, C.; Arnal, J. F.; Douin-Echinard, V.; Gourdy, P.; Guery, J. C. The TLR-mediated response of plasmacytoid dendritic cells is positively regulated by estradiol in vivo through cell-intrinsic estrogen receptor alpha signaling Journal Article In: Blood, vol. 119, no. 2, pp. 454-64, 2012, ISSN: 1528-0020 (Electronic)
0006-4971 (Linking). @article{RN9,
title = {The TLR-mediated response of plasmacytoid dendritic cells is positively regulated by estradiol in vivo through cell-intrinsic estrogen receptor alpha signaling},
author = {Seillet, C. and Laffont, S. and Tremollieres, F. and Rouquie, N. and Ribot, C. and Arnal, J. F. and Douin-Echinard, V. and Gourdy, P. and Guery, J. C.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22096248
http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/bloodjournal/119/2/454.full.pdf},
doi = {10.1182/blood-2011-08-371831},
issn = {1528-0020 (Electronic)
0006-4971 (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Blood},
volume = {119},
number = {2},
pages = {454-64},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Guery, J. C. Estrogens and inflammatory autoimmune diseases Journal Article In: Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme, vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 560-2, 2012, ISSN: 1778-7254 (Electronic)
1297-319X (Linking). @article{RN2b,
title = {Estrogens and inflammatory autoimmune diseases},
author = {Guery, J. C.},
url = {http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23141100},
doi = {10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.09.010},
issn = {1778-7254 (Electronic)
1297-319X (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme},
volume = {79},
number = {6},
pages = {560-2},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Boue, J.; Blanpied, C.; Djata-Cabral, M.; Pelletier, L.; Vergnolle, N.; Dietrich, G. Immune conditions associated with CD4+ T effector-induced opioid release and analgesia Journal Article In: Pain, vol. 153, no. 2, pp. 485-93, 2012, ISSN: 1872-6623 (Electronic)
0304-3959 (Linking). @article{RN18,
title = {Immune conditions associated with CD4+ T effector-induced opioid release and analgesia},
author = {Boue, J. and Blanpied, C. and Djata-Cabral, M. and Pelletier, L. and Vergnolle, N. and Dietrich, G.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22188867},
doi = {10.1016/j.pain.2011.11.013},
issn = {1872-6623 (Electronic)
0304-3959 (Linking)},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Pain},
volume = {153},
number = {2},
pages = {485-93},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
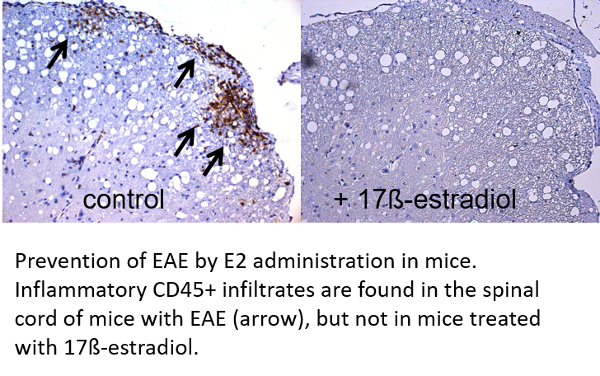 Clinical remissions in MS patients are frequent during pregnancy suggesting that hormones such as 17ß-estradiol (E2) could be protective. Indeed, beneficial effects of estrogen therapy have mainly been documented in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice and in MS patients.
Clinical remissions in MS patients are frequent during pregnancy suggesting that hormones such as 17ß-estradiol (E2) could be protective. Indeed, beneficial effects of estrogen therapy have mainly been documented in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice and in MS patients.