2023
|
Osma-Garcia, Ines C.; Mouysset, Mailys; Capitan-Sobrino, Dunja; Aubert, Yann; Turner, Martin; Diaz-Muñoz, Manuel D. The RNA binding proteins TIA1 and TIAL1 promote Mcl1 mRNA translation to protect germinal center responses from apoptosis Article de journal Dans: Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 2023, ISSN: 2042-0226. @article{Osma-Garcia2023b,
title = {The RNA binding proteins TIA1 and TIAL1 promote Mcl1 mRNA translation to protect germinal center responses from apoptosis},
author = {Osma-Garcia, Ines C.
and Mouysset, Mailys
and Capitan-Sobrino, Dunja
and Aubert, Yann
and Turner, Martin
and Diaz-Mu{ñ}oz, Manuel D.},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01063-4},
doi = {10.1038/s41423-023-01063-4},
issn = {2042-0226},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-07-20},
urldate = {2023-07-20},
journal = {Cellular & Molecular Immunology},
abstract = {Germinal centers (GCs) are essential for the establishment of long-lasting antibody responses. GC B cells rely on post-transcriptional RNA mechanisms to translate activation-associated transcriptional programs into functional changes in the cell proteome. However, the critical proteins driving these key mechanisms are still unknown. Here, we show that the RNA binding proteins TIA1 and TIAL1 are required for the generation of long-lasting GC responses. TIA1- and TIAL1-deficient GC B cells fail to undergo antigen-mediated positive selection, expansion and differentiation into B-cell clones producing high-affinity antibodies. Mechanistically, TIA1 and TIAL1 control the transcriptional identity of dark- and light-zone GC B cells and enable timely expression of the prosurvival molecule MCL1. Thus, we demonstrate here that TIA1 and TIAL1 are key players in the post-transcriptional program that selects high-affinity antigen-specific GC B cells.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Germinal centers (GCs) are essential for the establishment of long-lasting antibody responses. GC B cells rely on post-transcriptional RNA mechanisms to translate activation-associated transcriptional programs into functional changes in the cell proteome. However, the critical proteins driving these key mechanisms are still unknown. Here, we show that the RNA binding proteins TIA1 and TIAL1 are required for the generation of long-lasting GC responses. TIA1- and TIAL1-deficient GC B cells fail to undergo antigen-mediated positive selection, expansion and differentiation into B-cell clones producing high-affinity antibodies. Mechanistically, TIA1 and TIAL1 control the transcriptional identity of dark- and light-zone GC B cells and enable timely expression of the prosurvival molecule MCL1. Thus, we demonstrate here that TIA1 and TIAL1 are key players in the post-transcriptional program that selects high-affinity antigen-specific GC B cells. |
2022
|
Matheson, Louise S.; Petkau, Georg; S'aenz-Narciso, Beatriz; D'Angeli, Vanessa; McHugh, Jessica; Newman, Rebecca; Munford, Haydn; West, James; Chakraborty, Krishnendu; Roberts, Jennie; Łukasiak, Sebastian; D'iaz-Muñoz, Manuel D.; Bell, Sarah E.; Dimeloe, Sarah; Turner, Martin Multiomics analysis couples mRNA turnover and translational control of glutamine metabolism to the differentiation of the activated CD4+ T cell Article de journal Dans: Scientific Reports, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 19657, 2022, ISSN: 2045-2322. @article{Matheson2022,
title = {Multiomics analysis couples mRNA turnover and translational control of glutamine metabolism to the differentiation of the activated CD4+ T cell},
author = {Matheson, Louise S.
and Petkau, Georg
and S{'a}enz-Narciso, Beatriz
and D'Angeli, Vanessa
and McHugh, Jessica
and Newman, Rebecca
and Munford, Haydn
and West, James
and Chakraborty, Krishnendu
and Roberts, Jennie
and {Ł}ukasiak, Sebastian
and D{'i}az-Mu{ñ}oz, Manuel D.
and Bell, Sarah E.
and Dimeloe, Sarah
and Turner, Martin},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24132-6},
doi = {10.1038/s41598-022-24132-6},
issn = {2045-2322},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-11-16},
journal = {Scientific Reports},
volume = {12},
number = {1},
pages = {19657},
abstract = {The ZFP36 family of RNA-binding proteins acts post-transcriptionally to repress translation and promote RNA decay. Studies of genes and pathways regulated by the ZFP36 family in CD4+ T cells have focussed largely on cytokines, but their impact on metabolic reprogramming and differentiation is unclear. Using CD4+ T cells lacking Zfp36 and Zfp36l1, we combined the quantification of mRNA transcription, stability, abundance and translation with crosslinking immunoprecipitation and metabolic profiling to determine how they regulate T cell metabolism and differentiation. Our results suggest that ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 act directly to limit the expression of genes driving anabolic processes by two distinct routes: by targeting transcription factors and by targeting transcripts encoding rate-limiting enzymes. These enzymes span numerous metabolic pathways including glycolysis, one-carbon metabolism and glutaminolysis. Direct binding and repression of transcripts encoding glutamine transporter SLC38A2 correlated with increased cellular glutamine content in ZFP36/ZFP36L1-deficient T cells. Increased conversion of glutamine to $alpha$-ketoglutarate in these cells was consistent with direct binding of ZFP36/ZFP36L1 to Gls (encoding glutaminase) and Glud1 (encoding glutamate dehydrogenase). We propose that ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 as well as glutamine and $alpha$-ketoglutarate are limiting factors for the acquisition of the cytotoxic CD4+ T cell fate. Our data implicate ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 in limiting glutamine anaplerosis and differentiation of activated CD4+ T cells, likely mediated by direct binding to transcripts of critical genes that drive these processes.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The ZFP36 family of RNA-binding proteins acts post-transcriptionally to repress translation and promote RNA decay. Studies of genes and pathways regulated by the ZFP36 family in CD4+ T cells have focussed largely on cytokines, but their impact on metabolic reprogramming and differentiation is unclear. Using CD4+ T cells lacking Zfp36 and Zfp36l1, we combined the quantification of mRNA transcription, stability, abundance and translation with crosslinking immunoprecipitation and metabolic profiling to determine how they regulate T cell metabolism and differentiation. Our results suggest that ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 act directly to limit the expression of genes driving anabolic processes by two distinct routes: by targeting transcription factors and by targeting transcripts encoding rate-limiting enzymes. These enzymes span numerous metabolic pathways including glycolysis, one-carbon metabolism and glutaminolysis. Direct binding and repression of transcripts encoding glutamine transporter SLC38A2 correlated with increased cellular glutamine content in ZFP36/ZFP36L1-deficient T cells. Increased conversion of glutamine to $alpha$-ketoglutarate in these cells was consistent with direct binding of ZFP36/ZFP36L1 to Gls (encoding glutaminase) and Glud1 (encoding glutamate dehydrogenase). We propose that ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 as well as glutamine and $alpha$-ketoglutarate are limiting factors for the acquisition of the cytotoxic CD4+ T cell fate. Our data implicate ZFP36 and ZFP36L1 in limiting glutamine anaplerosis and differentiation of activated CD4+ T cells, likely mediated by direct binding to transcripts of critical genes that drive these processes. |
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Osma-Garcia, I. C. The RNA regulatory programs that govern lymphocyte development and function Article de journal Dans: Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, vol. 13, no. 1, p. e1683, 2022, ISSN: 1757-7012 (Electronic)
1757-7004 (Linking). @article{RN3b,
title = {The RNA regulatory programs that govern lymphocyte development and function},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Osma-Garcia, I. C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34327847},
doi = {10.1002/wrna.1683},
issn = {1757-7012 (Electronic)
1757-7004 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA},
volume = {13},
number = {1},
pages = {e1683},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Cacheiro-Llaguno, Cristina; Hernández-Subirá, Elena; Díaz-Muñoz, Manuel D.; Fresno, Manuel; Serrador, Juan M.; Íñiguez, Miguel A. Regulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human T Cells by Glucocorticoid Receptor-Mediated Transrepression of Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells Article de journal Dans: International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 23, no. 21, 2022, ISSN: 1422-0067. @article{ijms232113275,
title = {Regulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human T Cells by Glucocorticoid Receptor-Mediated Transrepression of Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells},
author = {Cacheiro-Llaguno, Cristina and Hernández-Subirá, Elena and Díaz-Muñoz, Manuel D. and Fresno, Manuel and Serrador, Juan M. and Íñiguez, Miguel A.},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/21/13275},
doi = {10.3390/ijms232113275},
issn = {1422-0067},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {International Journal of Molecular Sciences},
volume = {23},
number = {21},
abstract = {Cyclooxygenase (COX) is the key enzyme in prostanoid synthesis from arachidonic acid (AA). Two isoforms, named COX-1 and COX-2, are expressed in mammalian tissues. The expression of COX-2 isoform is induced by several stimuli including cytokines and mitogens, and this induction is inhibited by glucocorticoids (GCs). We have previously shown that the transcriptional induction of COX-2 occurs early after T cell receptor (TCR) triggering, suggesting functional implications of this enzyme in T cell activation. Here, we show that dexamethasone (Dex) inhibits nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)-mediated COX-2 transcriptional induction upon T cell activation. This effect is dependent on the presence of the GC receptor (GR), but independent of a functional DNA binding domain, as the activation-deficient GRLS7 mutant was as effective as the wild-type GR in the repression of NFAT-dependent transcription. Dex treatment did not disturb NFAT dephosphorylation, but interfered with activation mediated by the N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) of NFAT, thus pointing to a negative cross-talk between GR and NFAT at the nuclear level. These results unveil the ability of GCs to interfere with NFAT activation and the induction of pro-inflammatory genes such as COX-2, and explain some of their immunomodulatory properties in activated human T cells.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Cyclooxygenase (COX) is the key enzyme in prostanoid synthesis from arachidonic acid (AA). Two isoforms, named COX-1 and COX-2, are expressed in mammalian tissues. The expression of COX-2 isoform is induced by several stimuli including cytokines and mitogens, and this induction is inhibited by glucocorticoids (GCs). We have previously shown that the transcriptional induction of COX-2 occurs early after T cell receptor (TCR) triggering, suggesting functional implications of this enzyme in T cell activation. Here, we show that dexamethasone (Dex) inhibits nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)-mediated COX-2 transcriptional induction upon T cell activation. This effect is dependent on the presence of the GC receptor (GR), but independent of a functional DNA binding domain, as the activation-deficient GRLS7 mutant was as effective as the wild-type GR in the repression of NFAT-dependent transcription. Dex treatment did not disturb NFAT dephosphorylation, but interfered with activation mediated by the N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) of NFAT, thus pointing to a negative cross-talk between GR and NFAT at the nuclear level. These results unveil the ability of GCs to interfere with NFAT activation and the induction of pro-inflammatory genes such as COX-2, and explain some of their immunomodulatory properties in activated human T cells. |
Osma-Garcia, Ines C.; Capitan-Sobrino, Dunja; Mouysset, Mailys; Aubert, Yann; Maloudi, Orlane; Turner, Martin; Diaz-Muñoz, Manuel D. The splicing regulators TIA1 and TIAL1 are required for the expression of the DNA damage repair machinery during B cell lymphopoiesis Article de journal Dans: Cell Reports, vol. 41, no. 12, p. 111869, 2022, ISSN: 2211-1247. @article{OSMAGARCIA2022111869b,
title = {The splicing regulators TIA1 and TIAL1 are required for the expression of the DNA damage repair machinery during B cell lymphopoiesis},
author = {Ines C. Osma-Garcia and Dunja Capitan-Sobrino and Mailys Mouysset and Yann Aubert and Orlane Maloudi and Martin Turner and Manuel D. Diaz-Muñoz},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221112472201765X},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111869},
issn = {2211-1247},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Cell Reports},
volume = {41},
number = {12},
pages = {111869},
abstract = {Summary
B cell lymphopoiesis requires dynamic modulation of the B cell transcriptome for timely coordination of somatic mutagenesis and DNA repair in progenitor B (pro-B) cells. Here, we show that, in pro-B cells, the RNA-binding proteins T cell intracellular antigen 1 (TIA1) and TIA1-like protein (TIAL1) act redundantly to enable developmental progression. They are global splicing regulators that control the expression of hundreds of mRNAs, including those involved in DNA damage repair. Mechanistically, TIA1 and TIAL1 bind to 5′ splice sites for exon definition, splicing, and expression of DNA damage sensors, such as Chek2 and Rif1. In their absence, pro-B cells show exacerbated DNA damage, altered P53 expression, and increased cell death. Our study uncovers the importance of tight regulation of RNA splicing by TIA1 and TIAL1 for the expression of integrative transcriptional programs that control DNA damage sensing and repair during B cell development.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Summary
B cell lymphopoiesis requires dynamic modulation of the B cell transcriptome for timely coordination of somatic mutagenesis and DNA repair in progenitor B (pro-B) cells. Here, we show that, in pro-B cells, the RNA-binding proteins T cell intracellular antigen 1 (TIA1) and TIA1-like protein (TIAL1) act redundantly to enable developmental progression. They are global splicing regulators that control the expression of hundreds of mRNAs, including those involved in DNA damage repair. Mechanistically, TIA1 and TIAL1 bind to 5′ splice sites for exon definition, splicing, and expression of DNA damage sensors, such as Chek2 and Rif1. In their absence, pro-B cells show exacerbated DNA damage, altered P53 expression, and increased cell death. Our study uncovers the importance of tight regulation of RNA splicing by TIA1 and TIAL1 for the expression of integrative transcriptional programs that control DNA damage sensing and repair during B cell development. |
Hu, F.; Lu, J.; Matheson, L. S.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Saveliev, A.; Turner, M. Correction to: ORFLine: a bioinformatic pipeline to prioritize small open reading frames identifies candidate secreted small proteins from lymphocytes Article de journal Dans: Bioinformatics, 2022, ISSN: 1367-4811 (Electronic)
1367-4803 (Linking). @article{RN1b,
title = {Correction to: ORFLine: a bioinformatic pipeline to prioritize small open reading frames identifies candidate secreted small proteins from lymphocytes},
author = {Hu, F. and Lu, J. and Matheson, L. S. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Saveliev, A. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35349648},
doi = {10.1093/bioinformatics/btac162},
issn = {1367-4811 (Electronic)
1367-4803 (Linking)},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Bioinformatics},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2021
|
Belot, A.; Gourbeyre, O.; Palin, A.; Rubio, A.; Largounez, A.; Besson-Fournier, C.; Latour, C.; Lorgouilloux, M.; Gallitz, I.; Montagner, A.; Polizzi, A.; Regnier, M.; Smati, S.; Zhang, A. S.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Steinbicker, A. U.; Guillou, H.; Roth, M. P.; Coppin, H.; Meynard, D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress controls iron metabolism through TMPRSS6 repression and hepcidin mRNA stabilization by RNA-binding protein HuR Article de journal Dans: Haematologica, vol. 106, no. 4, p. 1202-1206, 2021, ISSN: 1592-8721 (Electronic)
0390-6078 (Linking). @article{RN6b,
title = {Endoplasmic reticulum stress controls iron metabolism through TMPRSS6 repression and hepcidin mRNA stabilization by RNA-binding protein HuR},
author = {Belot, A. and Gourbeyre, O. and Palin, A. and Rubio, A. and Largounez, A. and Besson-Fournier, C. and Latour, C. and Lorgouilloux, M. and Gallitz, I. and Montagner, A. and Polizzi, A. and Regnier, M. and Smati, S. and Zhang, A. S. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Steinbicker, A. U. and Guillou, H. and Roth, M. P. and Coppin, H. and Meynard, D.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32703788},
doi = {10.3324/haematol.2019.237321},
issn = {1592-8721 (Electronic)
0390-6078 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Haematologica},
volume = {106},
number = {4},
pages = {1202-1206},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Osma-Garcia, I. C.; Capitan-Sobrino, D.; Mouysset, M.; Bell, S. E.; Lebeurrier, M.; Turner, M.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D. The RNA-binding protein HuR is required for maintenance of the germinal centre response Article de journal Dans: Nat Commun, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 6556, 2021, ISSN: 2041-1723 (Electronic) 2041-1723 (Linking). @article{RN2,
title = {The RNA-binding protein HuR is required for maintenance of the germinal centre response},
author = {Osma-Garcia, I. C. and Capitan-Sobrino, D. and Mouysset, M. and Bell, S. E. and Lebeurrier, M. and Turner, M. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34772950},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-021-26908-2},
issn = {2041-1723 (Electronic) 2041-1723 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {12},
number = {1},
pages = {6556},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Mieulet, V.; Garnier, C.; Kieffer, Y.; Guilbert, T.; Nemati, F.; Marangoni, E.; Renault, G.; Chamming's, F.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. Stiffness increases with myofibroblast content and collagen density in mesenchymal high grade serous ovarian cancer Article de journal Dans: Sci Rep, vol. 11, no. 1, p. 4219, 2021, ISSN: 2045-2322 (Electronic)
2045-2322 (Linking). @article{RN30b,
title = {Stiffness increases with myofibroblast content and collagen density in mesenchymal high grade serous ovarian cancer},
author = {Mieulet, V. and Garnier, C. and Kieffer, Y. and Guilbert, T. and Nemati, F. and Marangoni, E. and Renault, G. and Chamming's, F. and Vincent-Salomon, A. and Mechta-Grigoriou, F.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33603134},
doi = {10.1038/s41598-021-83685-0},
issn = {2045-2322 (Electronic)
2045-2322 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Sci Rep},
volume = {11},
number = {1},
pages = {4219},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Hu, F.; Lu, J.; Matheson, L. S.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Saveliev, A.; Turner, M. ORFLine: a bioinformatic pipeline to prioritise small open reading frames identifies candidate secreted small proteins from lymphocytes Article de journal Dans: Bioinformatics, 2021, ISSN: 1367-4811 (Electronic)
1367-4803 (Linking). @article{RN4b,
title = {ORFLine: a bioinformatic pipeline to prioritise small open reading frames identifies candidate secreted small proteins from lymphocytes},
author = {Hu, F. and Lu, J. and Matheson, L. S. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Saveliev, A. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33970232},
doi = {10.1093/bioinformatics/btab339},
issn = {1367-4811 (Electronic)
1367-4803 (Linking)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Bioinformatics},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Boccasavia, V. L.; Bovolenta, E. R.; Villanueva, A.; Borroto, A.; Oeste, C. L.; van Santen, H. M.; Prieto, C.; Alonso-Lopez, D.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Batista, F. D.; Alarcon, B. Antigen presentation between T cells drives Th17 polarization under conditions of limiting antigen Article de journal Dans: Cell Rep, vol. 34, no. 11, p. 108861, 2021, ISSN: 2211-1247 (Electronic). @article{RN5b,
title = {Antigen presentation between T cells drives Th17 polarization under conditions of limiting antigen},
author = {Boccasavia, V. L. and Bovolenta, E. R. and Villanueva, A. and Borroto, A. and Oeste, C. L. and van Santen, H. M. and Prieto, C. and Alonso-Lopez, D. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Batista, F. D. and Alarcon, B.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33730591},
doi = {10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108861},
issn = {2211-1247 (Electronic)},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Cell Rep},
volume = {34},
number = {11},
pages = {108861},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2020
|
Lee, S.; Micalizzi, D.; Truesdell, S. S.; Bukhari, S. I. A.; Boukhali, M.; Lombardi-Story, J.; Kato, Y.; Choo, M. K.; Dey-Guha, I.; Ji, F.; Nicholson, B. T.; Myers, D. T.; Lee, D.; Mazzola, M. A.; Raheja, R.; Langenbucher, A.; Haradhvala, N. J.; Lawrence, M. S.; Gandhi, R.; Tiedje, C.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Sweetser, D. A.; Sadreyev, R.; Sykes, D.; Haas, W.; Haber, D. A.; Maheswaran, S.; Vasudevan, S. A post-transcriptional program of chemoresistance by AU-rich elements and TTP in quiescent leukemic cells Article de journal Dans: Genome Biol, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 33, 2020, ISSN: 1474-760X (Electronic)
1474-7596 (Linking). @article{RN7b,
title = {A post-transcriptional program of chemoresistance by AU-rich elements and TTP in quiescent leukemic cells},
author = {Lee, S. and Micalizzi, D. and Truesdell, S. S. and Bukhari, S. I. A. and Boukhali, M. and Lombardi-Story, J. and Kato, Y. and Choo, M. K. and Dey-Guha, I. and Ji, F. and Nicholson, B. T. and Myers, D. T. and Lee, D. and Mazzola, M. A. and Raheja, R. and Langenbucher, A. and Haradhvala, N. J. and Lawrence, M. S. and Gandhi, R. and Tiedje, C. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Sweetser, D. A. and Sadreyev, R. and Sykes, D. and Haas, W. and Haber, D. A. and Maheswaran, S. and Vasudevan, S.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32039742},
doi = {10.1186/s13059-020-1936-4},
issn = {1474-760X (Electronic)
1474-7596 (Linking)},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Genome Biol},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {33},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2019
|
Gentric, G.; Kieffer, Y.; Mieulet, V.; Goundiam, O.; Bonneau, C.; Nemati, F.; Hurbain, I.; Raposo, G.; Popova, T.; Stern, M. H.; Lallemand-Breitenbach, V.; Muller, S.; Caneque, T.; Rodriguez, R.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; de The, H.; Rossignol, R.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. PML-Regulated Mitochondrial Metabolism Enhances Chemosensitivity in Human Ovarian Cancers Article de journal Dans: Cell Metab, vol. 29, no. 1, p. 156-173 e10, 2019, ISSN: 1932-7420 (Electronic)
1550-4131 (Linking). @article{RN31b,
title = {PML-Regulated Mitochondrial Metabolism Enhances Chemosensitivity in Human Ovarian Cancers},
author = {Gentric, G. and Kieffer, Y. and Mieulet, V. and Goundiam, O. and Bonneau, C. and Nemati, F. and Hurbain, I. and Raposo, G. and Popova, T. and Stern, M. H. and Lallemand-Breitenbach, V. and Muller, S. and Caneque, T. and Rodriguez, R. and Vincent-Salomon, A. and de The, H. and Rossignol, R. and Mechta-Grigoriou, F.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30244973},
doi = {10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.002},
issn = {1932-7420 (Electronic)
1550-4131 (Linking)},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Cell Metab},
volume = {29},
number = {1},
pages = {156-173 e10},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Trulley, P.; Snieckute, G.; Bekker-Jensen, D.; Menon, M. B.; Freund, R.; Kotlyarov, A.; Olsen, J. V.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Turner, M.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Gaestel, M.; Tiedje, C. Alternative Translation Initiation Generates a Functionally Distinct Isoform of the Stress-Activated Protein Kinase MK2 Article de journal Dans: Cell Rep, vol. 27, no. 10, p. 2859-2870 e6, 2019, ISSN: 2211-1247 (Electronic). @article{RN8b,
title = {Alternative Translation Initiation Generates a Functionally Distinct Isoform of the Stress-Activated Protein Kinase MK2},
author = {Trulley, P. and Snieckute, G. and Bekker-Jensen, D. and Menon, M. B. and Freund, R. and Kotlyarov, A. and Olsen, J. V. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Turner, M. and Bekker-Jensen, S. and Gaestel, M. and Tiedje, C.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31167133},
doi = {10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.024},
issn = {2211-1247 (Electronic)},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Cell Rep},
volume = {27},
number = {10},
pages = {2859-2870 e6},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2018
|
Turner, M.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D. RNA-binding proteins control gene expression and cell fate in the immune system Article de journal Dans: Nat Immunol, vol. 19, no. 2, p. 120-129, 2018, ISSN: 1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking). @article{RN12b,
title = {RNA-binding proteins control gene expression and cell fate in the immune system},
author = {Turner, M. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29348497},
doi = {10.1038/s41590-017-0028-4},
issn = {1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Nat Immunol},
volume = {19},
number = {2},
pages = {120-129},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Monzon-Casanova, E.; Screen, M.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Coulson, R. M. R.; Bell, S. E.; Lamers, G.; Solimena, M.; Smith, C. W. J.; Turner, M. The RNA-binding protein PTBP1 is necessary for B cell selection in germinal centers Article de journal Dans: Nat Immunol, vol. 19, no. 3, p. 267-278, 2018, ISSN: 1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking). @article{RN11b,
title = {The RNA-binding protein PTBP1 is necessary for B cell selection in germinal centers},
author = {Monzon-Casanova, E. and Screen, M. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Coulson, R. M. R. and Bell, S. E. and Lamers, G. and Solimena, M. and Smith, C. W. J. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29358707},
doi = {10.1038/s41590-017-0035-5},
issn = {1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Nat Immunol},
volume = {19},
number = {3},
pages = {267-278},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Mendoza, P.; Martinez-Martin, N.; Bovolenta, E. R.; Reyes-Garau, D.; Hernansanz-Agustin, P.; Delgado, P.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Oeste, C. L.; Fernandez-Pisonero, I.; Castellano, E.; Martinez-Ruiz, A.; Alonso-Lopez, D.; Santos, E.; Bustelo, X. R.; Kurosaki, T.; Alarcon, B. R-Ras2 is required for germinal center formation to aid B cells during energetically demanding processes Article de journal Dans: Sci Signal, vol. 11, no. 532, 2018, ISSN: 1937-9145 (Electronic)
1945-0877 (Linking). @article{RN10b,
title = {R-Ras2 is required for germinal center formation to aid B cells during energetically demanding processes},
author = {Mendoza, P. and Martinez-Martin, N. and Bovolenta, E. R. and Reyes-Garau, D. and Hernansanz-Agustin, P. and Delgado, P. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Oeste, C. L. and Fernandez-Pisonero, I. and Castellano, E. and Martinez-Ruiz, A. and Alonso-Lopez, D. and Santos, E. and Bustelo, X. R. and Kurosaki, T. and Alarcon, B.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29844052},
doi = {10.1126/scisignal.aal1506},
issn = {1937-9145 (Electronic)
1945-0877 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Sci Signal},
volume = {11},
number = {532},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Givel, A. M.; Kieffer, Y.; Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Sirven, P.; Cardon, M.; Pelon, F.; Magagna, I.; Gentric, G.; Costa, A.; Bonneau, C.; Mieulet, V.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. miR200-regulated CXCL12beta promotes fibroblast heterogeneity and immunosuppression in ovarian cancers Article de journal Dans: Nat Commun, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 1056, 2018, ISSN: 2041-1723 (Electronic)
2041-1723 (Linking). @article{RN32,
title = {miR200-regulated CXCL12beta promotes fibroblast heterogeneity and immunosuppression in ovarian cancers},
author = {Givel, A. M. and Kieffer, Y. and Scholer-Dahirel, A. and Sirven, P. and Cardon, M. and Pelon, F. and Magagna, I. and Gentric, G. and Costa, A. and Bonneau, C. and Mieulet, V. and Vincent-Salomon, A. and Mechta-Grigoriou, F.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29535360},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-018-03348-z},
issn = {2041-1723 (Electronic)
2041-1723 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {9},
number = {1},
pages = {1056},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Turner, M. Uncovering the Role of RNA-Binding Proteins in Gene Expression in the Immune System Article de journal Dans: Front Immunol, vol. 9, p. 1094, 2018, ISSN: 1664-3224 (Print)
1664-3224 (Linking). @article{RN9b,
title = {Uncovering the Role of RNA-Binding Proteins in Gene Expression in the Immune System},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29875770},
doi = {10.3389/fimmu.2018.01094},
issn = {1664-3224 (Print)
1664-3224 (Linking)},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Front Immunol},
volume = {9},
pages = {1094},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2017
|
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Monzon-Casanova, E.; Turner, M. Characterization of the B Cell Transcriptome Bound by RNA-Binding Proteins with iCLIP Article de journal Dans: Methods Mol Biol, vol. 1623, p. 159-179, 2017, ISSN: 1940-6029 (Electronic)
1064-3745 (Linking). @article{RN14b,
title = {Characterization of the B Cell Transcriptome Bound by RNA-Binding Proteins with iCLIP},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Monzon-Casanova, E. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28589356},
doi = {10.1007/978-1-4939-7095-7_14},
issn = {1940-6029 (Electronic)
1064-3745 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Methods Mol Biol},
volume = {1623},
pages = {159-179},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Kiselev, V. Y.; Le Novere, N.; Curk, T.; Ule, J.; Turner, M. Tia1 dependent regulation of mRNA subcellular location and translation controls p53 expression in B cells Article de journal Dans: Nat Commun, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 530, 2017, ISSN: 2041-1723 (Electronic)
2041-1723 (Linking). @article{RN13b,
title = {Tia1 dependent regulation of mRNA subcellular location and translation controls p53 expression in B cells},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Kiselev, V. Y. and Le Novere, N. and Curk, T. and Ule, J. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28904350},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-017-00454-2},
issn = {2041-1723 (Electronic)
2041-1723 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {8},
number = {1},
pages = {530},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2016
|
Tiedje, C.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Trulley, P.; Ahlfors, H.; Laass, K.; Blackshear, P. J.; Turner, M.; Gaestel, M. The RNA-binding protein TTP is a global post-transcriptional regulator of feedback control in inflammation Article de journal Dans: Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 44, no. 15, p. 7418-40, 2016, ISSN: 1362-4962 (Electronic)
0305-1048 (Linking). @article{RN15b,
title = {The RNA-binding protein TTP is a global post-transcriptional regulator of feedback control in inflammation},
author = {Tiedje, C. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Trulley, P. and Ahlfors, H. and Laass, K. and Blackshear, P. J. and Turner, M. and Gaestel, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27220464},
doi = {10.1093/nar/gkw474},
issn = {1362-4962 (Electronic)
0305-1048 (Linking)},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Nucleic Acids Res},
volume = {44},
number = {15},
pages = {7418-40},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Galloway, A.; Saveliev, A.; Lukasiak, S.; Hodson, D. J.; Bolland, D.; Balmanno, K.; Ahlfors, H.; Monzon-Casanova, E.; Mannurita, S. C.; Bell, L. S.; Andrews, S.; Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Cook, S. J.; Corcoran, A.; Turner, M. RNA-binding proteins ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 promote cell quiescence Article de journal Dans: Science, vol. 352, no. 6284, p. 453-9, 2016, ISSN: 1095-9203 (Electronic)
0036-8075 (Linking). @article{RN16b,
title = {RNA-binding proteins ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 promote cell quiescence},
author = {Galloway, A. and Saveliev, A. and Lukasiak, S. and Hodson, D. J. and Bolland, D. and Balmanno, K. and Ahlfors, H. and Monzon-Casanova, E. and Mannurita, S. C. and Bell, L. S. and Andrews, S. and Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Cook, S. J. and Corcoran, A. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27102483},
doi = {10.1126/science.aad5978},
issn = {1095-9203 (Electronic)
0036-8075 (Linking)},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Science},
volume = {352},
number = {6284},
pages = {453-9},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
2015
|
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Bell, S. E.; Turner, M. Deletion of AU-rich elements within the Bcl2 3'UTR reduces protein expression and B cell survival in vivo Article de journal Dans: PLoS One, vol. 10, no. 2, p. e0116899, 2015, ISSN: 1932-6203 (Electronic)
1932-6203 (Linking). @article{RN20b,
title = {Deletion of AU-rich elements within the Bcl2 3'UTR reduces protein expression and B cell survival in vivo},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Bell, S. E. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25680182},
doi = {10.1371/journal.pone.0116899},
issn = {1932-6203 (Electronic)
1932-6203 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {PLoS One},
volume = {10},
number = {2},
pages = {e0116899},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
Diaz-Munoz, M. D.; Bell, S. E.; Fairfax, K.; Monzon-Casanova, E.; Cunningham, A. F.; Gonzalez-Porta, M.; Andrews, S. R.; Bunik, V. I.; Zarnack, K.; Curk, T.; Heggermont, W. A.; Heymans, S.; Gibson, G. E.; Kontoyiannis, D. L.; Ule, J.; Turner, M. The RNA-binding protein HuR is essential for the B cell antibody response Article de journal Dans: Nat Immunol, vol. 16, no. 4, p. 415-25, 2015, ISSN: 1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking). @article{RN19b,
title = {The RNA-binding protein HuR is essential for the B cell antibody response},
author = {Diaz-Munoz, M. D. and Bell, S. E. and Fairfax, K. and Monzon-Casanova, E. and Cunningham, A. F. and Gonzalez-Porta, M. and Andrews, S. R. and Bunik, V. I. and Zarnack, K. and Curk, T. and Heggermont, W. A. and Heymans, S. and Gibson, G. E. and Kontoyiannis, D. L. and Ule, J. and Turner, M.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25706746},
doi = {10.1038/ni.3115},
issn = {1529-2916 (Electronic)
1529-2908 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {Nat Immunol},
volume = {16},
number = {4},
pages = {415-25},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
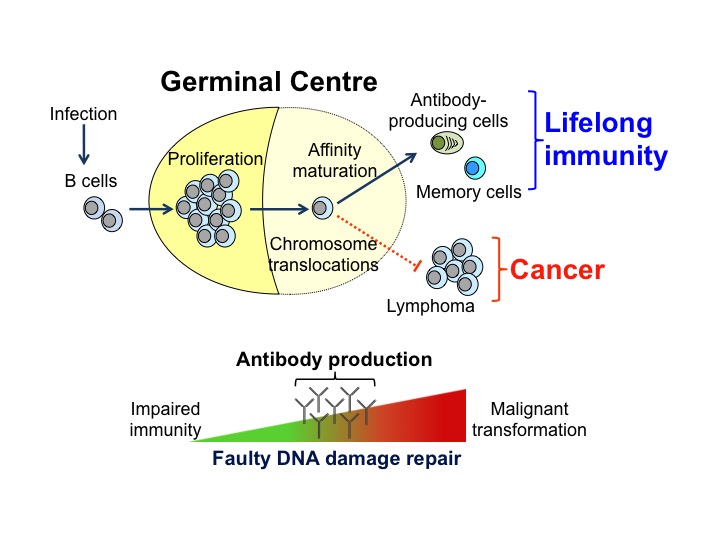 La formation des centres germinatifs (GC) est une caractéristique de la lutte contre les pathogènes, mais ceux-ci sont aussi la source de la plupart des lymphomes B non hodgkiniens. Les GC sont des structures anatomiques distinctes qui se forment dans les organes lymphoïdes secondaires, tels que la rate et les ganglions lymphatiques lors d’une l’infection par un pathogène. Ils ne constituent pas seulement des sites où se déroule l’expansion clonale des lymphocytes B, mais aussi où le répertoire d’anticorps se diversifie. En effet, dans les GC, les lymphocytes B subissent une maturation d’affinité qui correspond à la mutation des gènes codant pour les immunoglobulines (Ig) qui est suivie par la sélection des cellules exprimant des immunoglobulines d’affinité augmentée. Ce processus génère les cellules productrices d’anticorps et des lymphocytes B mémoires qui protègent contre les infections récurrentes. Un contrôle strict de l’hypermutation somatique des Ig et de la réparation des lésions de l’ADN est essentiel à la production d’anticorps. En effet des mutations mal ciblées peuvent conduire à des translocations chromosomiques et à une transformation tumorale des lymphocytes B.
La formation des centres germinatifs (GC) est une caractéristique de la lutte contre les pathogènes, mais ceux-ci sont aussi la source de la plupart des lymphomes B non hodgkiniens. Les GC sont des structures anatomiques distinctes qui se forment dans les organes lymphoïdes secondaires, tels que la rate et les ganglions lymphatiques lors d’une l’infection par un pathogène. Ils ne constituent pas seulement des sites où se déroule l’expansion clonale des lymphocytes B, mais aussi où le répertoire d’anticorps se diversifie. En effet, dans les GC, les lymphocytes B subissent une maturation d’affinité qui correspond à la mutation des gènes codant pour les immunoglobulines (Ig) qui est suivie par la sélection des cellules exprimant des immunoglobulines d’affinité augmentée. Ce processus génère les cellules productrices d’anticorps et des lymphocytes B mémoires qui protègent contre les infections récurrentes. Un contrôle strict de l’hypermutation somatique des Ig et de la réparation des lésions de l’ADN est essentiel à la production d’anticorps. En effet des mutations mal ciblées peuvent conduire à des translocations chromosomiques et à une transformation tumorale des lymphocytes B.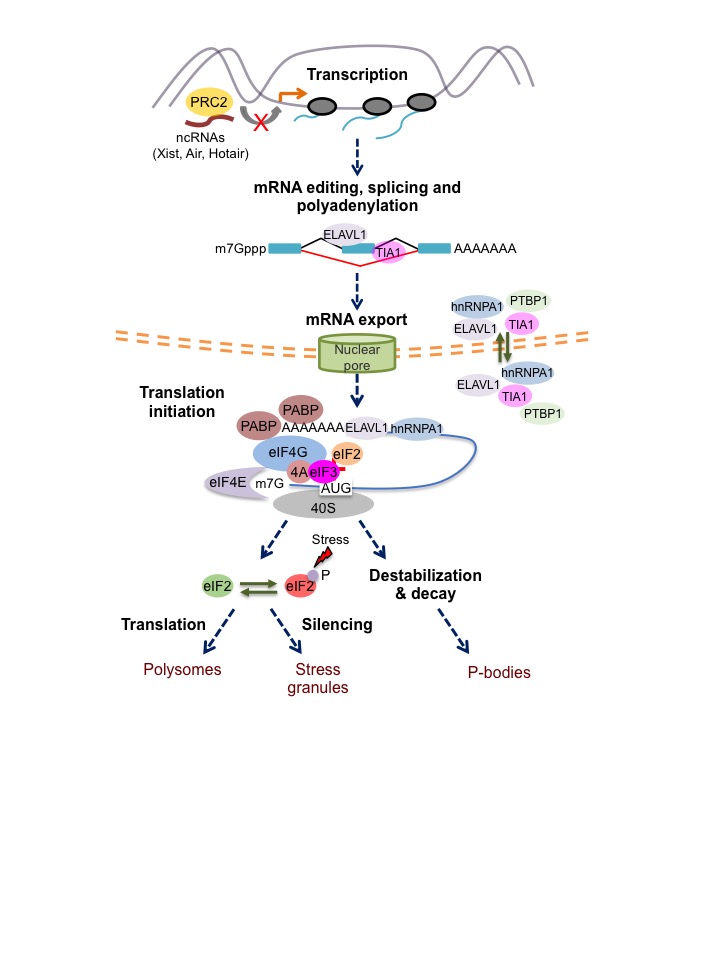
 Comprendre la régulation du développement et de la différenciation lymphocytaire nécessite une analyse approfondie du génome cellulaire, du transcriptome et du translatome. Le développement des techniques de séquençage de nouvelle génération (NGS) a révélé des réseaux de molécules d’ARNm qui réagissent de manière similaire à un stimulus donné. Ces avancées technologiques ont permis de déchiffrer les propriétés de liaison à l’ARN de centaines de protéines et d’identifier l’ensemble des protéines de liaison à l’ARN associées à un seul transcrit. L’interprétation et l’intégration de ces données globales pour comprendre la régulation du développement des lymphocytes est un des grands objectifs de notre laboratoire.
Comprendre la régulation du développement et de la différenciation lymphocytaire nécessite une analyse approfondie du génome cellulaire, du transcriptome et du translatome. Le développement des techniques de séquençage de nouvelle génération (NGS) a révélé des réseaux de molécules d’ARNm qui réagissent de manière similaire à un stimulus donné. Ces avancées technologiques ont permis de déchiffrer les propriétés de liaison à l’ARN de centaines de protéines et d’identifier l’ensemble des protéines de liaison à l’ARN associées à un seul transcrit. L’interprétation et l’intégration de ces données globales pour comprendre la régulation du développement des lymphocytes est un des grands objectifs de notre laboratoire.





